| 编辑推荐: |
本文从主要对Android组件化框架项目进行详解,并附有代码和示例,希望对您的学习有所帮助。
本文来自于csdn,由火龙果软件Alice编辑、推荐。 |
|
简介
什么是组件化?
项目发展到一定阶段时,随着需求的增加以及频繁地变更,项目会越来越大,代码变得越来越臃肿,耦合会越来越多,开发效率也会降低,这个时候我们就需要对旧项目进行重构即模块的拆分,官方的说法就是组件化。
组件化带来的好处
那么,采用组件化能带来什么好处呢?主要有以下两点:
1、现在Android项目中代码量达到一定程度,编译将是一件非常痛苦的事情,一般都需要编译5到6分钟。Android
Studio 推出 instant run 由于各种缺陷和限制条件(比如采用热修复tinker)一般情况下是被关闭的。而组件化框架可以使模块单独编译调试,可以有效地减少编译的时间。
2、通过组件化可以更好的进行并行开发,因为我们可以为每一个模块进行单独的版本控制,甚至每一个模块的负责人可以选择自己的设计架构而不影响其他模块的开发,与此同时组件化还可以避免模块之间的交叉依赖,每一个模块的开发人员可以对自己的模块进行独立测试,独立编译和运行,甚至可以实现单独的部署。从而极大的提高了并行开发效率。
组件化框架
来看组件化一个简单的例子,图例如下:
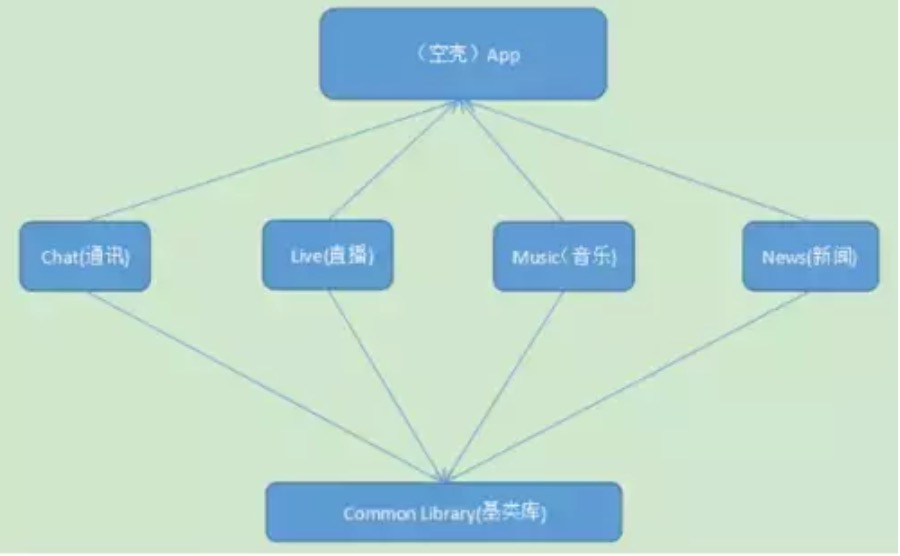
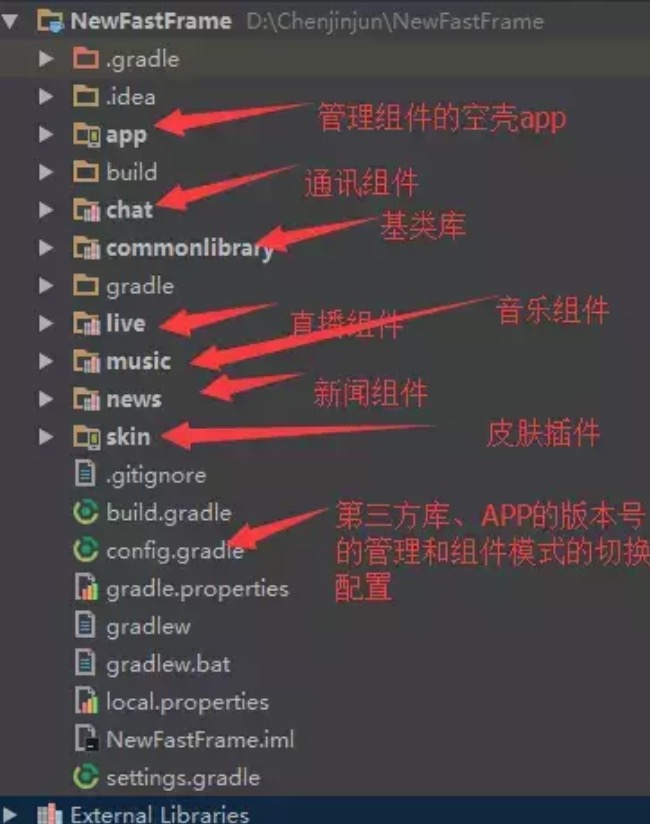
基类库的封装
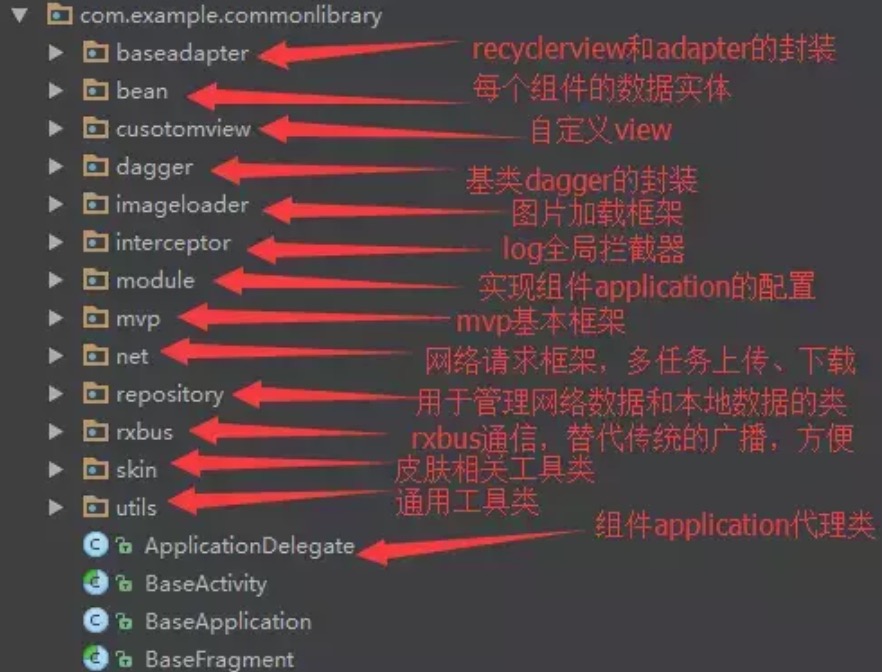
对于Android中常用的基类库,主要包括开发常用的一些框架。
1、网络请求(多任务下载和上传,采用 Retrofit+RxJava 框架)
2、图片加载(策略模式,Glide 与 Picasso 之间可以切换)
3、通信机制(RxBus)
4、基类 adapter 的封装(支持 item动画、多布局item、下拉和加载更多、item点击事件)
5、基类 RecyclerView 的封装(支持原生风格的下拉加载,item侧滑等)
6、mvp 框架
7、各组件的数据库实体类
8、通用的工具类
9、自定义view(包括对话框,ToolBar布局,圆形图片等view的自定义)
10、dagger 的封装(用于初始化全局的变量和网络请求等配置)
11、其他等等
组件模式和集成模式切换的实现
music组件 下的 build.gradle 文件,其他组件类似。
//控制组件模式和集成模式
if (rootProject.ext.isAlone) {
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
} else {
apply plugin: 'com.android.library' }
apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt'
android {
compileSdkVersion rootProject.ext.android.
compileSdkVersion
buildToolsVersion rootProject.ext.android.
buildToolsVersion
defaultConfig {
if (rootProject.ext.isAlone) {
//组件模式下设置applicationId
applicationId "com.example.cootek.music"
}
minSdkVersion rootProject.
ext.android.minSdkVersion
targetSdkVersion rootProject.ext.android.
targetSdkVersion
versionCode rootProject.
ext.android.versionCode
versionName rootProject.ext.android.versionName
testInstrumentationRunner "android.
support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
if (!rootProject.ext.isAlone) {
//集成模式下Arouter的配置,用于组件间通信的实现
javaCompileOptions {
annotationProcessorOptions {
arguments = [moduleName: project.getName()]
}
}
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile
('proguard-android.txt'),
'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_7
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_7
}
sourceSets {
main {
//控制两种模式下的资源和代码配置情况
if (rootProject.ext.isAlone) {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/module/AndroidManifest.xml'
java.srcDirs = ['src/main/java', 'src/main/module/java']
res.srcDirs = ['src/main/res', 'src/main/module/res']
} else {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/AndroidManifest.xml'
}
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
androidTestCompile('com.android.support<br>.
test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2',
{
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module:
'support-annotations'
})
//依赖基类库
compile project(':commonlibrary')
//用作颜色选择器
compile 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:
commons:0.9.1.0'
apt rootProject.ext.dependencies.dagger2_compiler
if (!rootProject.ext.isAlone) {
//集成模式下需要编译器生成路由通信的代码
apt rootProject.ext.dependencies.arouter_compiler
}
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
}
|
为了区分集成模式和组件模式,我们使用isAlone变量来控制。
集成模式
1、首先需要在 config.gradle 文件中设置 isAlone = false。形如:
ext {
isAlone = false; //false:作为Lib组件存在,
true:作为application存在 |
2、然后 Sync 下。
3、最后选择 app 运行即可。
组件模式
1、首先需要在 config.gradle 文件中设置 isAlone = true
2、然后 Sync 下。
3、最后相应的模块(new、chat、live、music、app)进行运行即可。
config.gradle 文件的配置情况如下:
ext {
isAlone = false;//false:作为集成模式存在,
true:作为组件模式存在
// 各个组件版本号的统一管理
android = [
compileSdkVersion: 24,
buildToolsVersion: "25.0.2",
minSdkVersion : 16,
targetSdkVersion : 22,
versionCode : 1,
versionName : '1.0.0',
]
libsVersion = [
// 第三方库版本号的管理
supportLibraryVersion = "25.3.0",
retrofitVersion = "2.1.0",
glideVersion = "3.7.0",
loggerVersion = "1.15",
// eventbusVersion = "3.0.0",
gsonVersion = "2.8.0",
butterknife = "8.8.0",
retrofit = "2.3.0",
rxjava = "2.1.1",
rxjava_android = "2.0.1",
rxlifecycle = "2.1.0",
rxlifecycle_components = "2.1.0",
dagger_compiler = "2.11",
dagger = "2.11",
greenDao = "3.2.2",
arouter_api = "1.2.2",
arouter_compiler = "1.1.3",
transformations = "2.0.2",
rxjava_adapter = "2.3.0",
gson_converter = "2.3.0",
scalars_converter = "2.3.0",
rxpermission = "0.9.4",
eventbus="3.0.0",
support_v4="25.4.0",
okhttp3="3.8.1"
]
// 依赖库管理
dependencies = [
appcompatV7 : "com.android.support:appcompat-v7:$rootProject.supportLibraryVersion",
design : "com.android.support:design:$rootProject.
supportLibraryVersion",
cardview : "com.android.support:cardview-v7:
$rootProject.supportLibraryVersion",
palette : "com.android.support:palette-v7:
$rootProject.supportLibraryVersion",
recycleview : "com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:
$rootProject.supportLibraryVersion",
support_v4 : "com.android.support:support-v4:
$rootProject.support_v4",
annotations : "com.android.support:
support-annotations:$rootProject.supportLibraryVersion",
eventBus : "org.greenrobot:eventbus:
$rootProject.eventbus",
glide : "com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:$rootProject.
glideVersion",
gson : "com.google.code.gson:gson:$rootProject.
gsonVersion",
logger : "com.orhanobut:logger:
$rootProject.loggerVersion",
butterknife :
"com.jakewharton:butterknife:
$rootProject.butterknife",
butterknife_compiler : "com.jakewharton:
butterknife-compiler:$rootProject.butterknife",
retrofit : "com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:
$rootProject.retrofit",
okhttp3 : "com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:$rootProject.retrofit",
retrofit_adapter_rxjava2 : "com.squareup.
retrofit2:adapter-rxjava2:$rootProject.rxjava_adapter",
retrofit_converter_gson : "com.squareup.
retrofit2:converter-gson:$rootProject.gson_converter",
retrofit_converter_scalars: "com.squareup.
retrofit2:converter-scalars:$rootProject.scalars_converter",
rxpermission : "com.tbruyelle.rxpermissions2:
rxpermissions:$rootProject.rxpermission@aar",
rxjava2 : "io.reactivex.rxjava2:rxjava:$rootProject.rxjava",
rxjava2_android : "io.reactivex.rxjava2:
rxandroid:$rootProject.rxjava_android",
rxlifecycle2 : "com.trello.rxlifecycle2:
rxlifecycle:$rootProject.rxlifecycle",
rxlifecycle2_components : "com.trello.
rxlifecycle2:rxlifecycle-components:
$rootProject.rxlifecycle_components",
dagger2_compiler : "com.google.dagger:
dagger-compiler:$rootProject.dagger_compiler",
dagger2 : "com.google.dagger:dagger:
$rootProject.dagger",
greenDao : "org.greenrobot:greendao:$rootProject.greenDao",
transformations : "jp.wasabeef:glide-transformations:
$rootProject.transformations",
//路由通讯
arouter_api : "com.alibaba:arouter-api:
$rootProject.arouter_api",
arouter_compiler :
"com.alibaba:arouter-compiler:
$rootProject.arouter_compiler"
]
}
|
组件间通信实现
组件间通信的实现可以使用阿里开源的 Arouter 路由通信。相关内容可以查看:https://github.com/alibaba/ARouter。
首先,初始化所有的数据信息。
private List<MainItemBean>
getDefaultData() {
List<MainItemBean> result = new ArrayList<>();
MainItemBean mainItemBean = new MainItemBean();
mainItemBean.setName("校园");
mainItemBean.setPath("/news/main");
mainItemBean.setResId(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
MainItemBean music=new MainItemBean();
music.setName("音乐");
music.setResId(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
music.setPath("/music/main");
MainItemBean live = new MainItemBean();
live.setName("直播");
live.setResId(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
live.setPath("/live/main");
MainItemBean chat = new MainItemBean();
chat.setName("聊天");
chat.setPath("/chat/splash");
chat.setResId(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
result.add(mainItemBean);
result.add(music);
result.add(live);
result.add(chat);
return result;
}
|
然后在设置每个 item 的点击事件时,启动组件界面跳转。
@Override
public void onItemClick(int position, View view)
{
MainItemBean item=mainAdapter.getData(position);
ARouter.getInstance().build(item.getPath()).navigation();
}
|
每个组件入口界面的设置(比如直播 Live 组件,其它组件类似)。
@Route(path =
"/live/main")
public class MainActivity extends BaseActivity<
List<CategoryLiveBean>,
MainPresenter>
implements View.OnClickListener
{
//
}
|
res资源和AndroidManifest配置
我们通过判断组件处于哪种模式来动态设置项目res资源和Manifest、以及代码的位置。以直播组件为例,其它组件类似。
作为一个组件模块后,再来看一下直播组件的 build.gradle 文件对代码资源等位置的配置。
sourceSets {
main {
if (rootProject.ext.isAlone) {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/module/AndroidManifest.xml'
java.srcDirs = ['src/main/java', 'src/main/module/java']
res.srcDirs = ['src/main/res', 'src/main/module/res']
} else {
manifest.srcFile 'src/main/AndroidManifest.xml'
}
}
}
|
全局application的实现和数据的初始化
采用类似于 Glide 在 Manifest 初始化配置的方式来初始化各个组件的 Application,下面以直播组件为例来完成初始化,其它类似。
在 BaseApplication 中,初始化 ApplicationDelegate 代理类。
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base)
{
super.attachBaseContext(base);
applicationDelegate = new ApplicationDelegate();
applicationDelegate.attachBaseContext(base);
MultiDex.install(this);
}
|
ApplicationDelegate 内部是怎样的呢,看一段源码。
public class
ApplicationDelegate implements IAppLife {
private List<IModuleConfig> list;
private List<IAppLife> appLifes;
private List<Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks>
liferecycleCallbacks;
public ApplicationDelegate() {
appLifes = new ArrayList<>();
liferecycleCallbacks = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public void attachBaseContext(Context base)
{
//初始化Manifest文件解析器,用于解析组件
在自己的Manifest文件配置的Application
ManifestParser manifestParser = new ManifestParser(base);
list = manifestParser.parse();
//解析得到的组件Application列表之后,
给每个组件Application注入
//context,和Application的生命周期的回调,
用于实现application的同步
if (list != null && list.size() >
0) {
for (IModuleConfig configModule :
list) {
configModule.injectAppLifecycle(base, appLifes);
configModule.injectActivityLifecycle(base,
liferecycleCallbacks);
}
}
if (appLifes != null && appLifes.size()
> 0) {
for (IAppLife life :
appLifes) {
life.attachBaseContext(base);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Application application)
{
//相应调用组件Application代理类的onCreate方法
if (appLifes != null && appLifes.size()
> 0) {
for (IAppLife life :
appLifes) {
life.onCreate(application);
}
}
if (liferecycleCallbacks != null &&
liferecycleCallbacks.size() > 0) {
for (Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks
life :
liferecycleCallbacks) {
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(life);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onTerminate(Application application)
{
//相应调用组件Application代理类的onTerminate方法
if (appLifes != null && appLifes.size()
> 0) {
for (IAppLife life :
appLifes) {
life.onTerminate(application);
}
}
if (liferecycleCallbacks != null &&
liferecycleCallbacks.size() > 0) {
for (Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks
life :
liferecycleCallbacks) {
application.unregisterActivityLifecycleCallbacks(life);
}
}
}
}
|
组件 Manifest 中 application 的全局配置如下:
<meta-data
android:name="com.example.live.LiveApplication"
android:value="IModuleConfig" />
|
ManifestParser 会对其中 value 为 IModuleConfig 的 meta-data
进行解析,并通过反射生成实例。
public final
class ManifestParser {
private static final String MODULE_VALUE
= "IModuleConfig";
private final Context context;
public ManifestParser(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public List<IModuleConfig> parse() {
List<IModuleConfig> modules = new ArrayList<>();
try {
ApplicationInfo appInfo = context.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
context.getPackageName(), PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
if (appInfo.metaData != null) {
for (String key : appInfo.metaData.keySet()) {
//会对其中value为IModuleConfig的meta-data进行解析,
并通过反射生成实例
if (MODULE_VALUE.equals(appInfo.metaData.get(key)))
{
modules.add(parseModule(key));
}
}
}
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException
e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to find
metadata to parse IModuleConfig", e);
}
return modules;
}
//通过类名生成实例
private static IModuleConfig parseModule(String
className) {
Class<?> clazz;
try {
clazz = Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable
to find
IModuleConfig implementation",
e);
}
Object module;
try {
module = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to
instantiate
IModuleConfig implementation for " + clazz,
e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate
IModuleConfig implementation for " + clazz,
e);
}
if (!(module instanceof IModuleConfig)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Expected instanceof
IModuleConfig, but found: " + module);
}
return (IModuleConfig) module;
}
}
|
这样通过以上步骤就可以在 Manifest 文件中配置自己组件的 Application,用于初始化组件内的数据,比如在直播组件中初始化
Dagger注解 的全局配置。
public class
LiveApplication implements IModuleConfig,
IAppLife
{
private static MainComponent mainComponent;
@Override
public void injectAppLifecycle(Context context,
List<IAppLife> iAppLifes) {
//这里需要把本引用添加到Application的生命周期的回调中,
以便实现回调
iAppLifes.add(this);
}
@Override
public void injectActivityLifecycle(Context
context, List<Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks>
lifecycleCallbackses) {
}
@Override
public void attachBaseContext(Context base)
{
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Application application)
{
//在onCreate方法中对Dagger进行初始化
mainComponent = DaggerMainComponent.builder().
mainModule(new
MainModule())
.appComponent(BaseApplication.getAppComponent()).build();
}
@Override
public void onTerminate(Application application)
{
if (mainComponent != null) {
mainComponent = null;
}
}
public static MainComponent getMainComponent()
{
return mainComponent;
}
}
|
组件内网络请求和拦截器
由于每个组件的 BaseUrl 和网络配置等可能不一样,所以每个组件可以在自己配置的 dagger
中的 MainConponent 实现自己的网络请求和拦截器。以直播为例,部分代码内容如下:
@PerApplication
@Component(dependencies = AppComponent.class,
modules = MainModule.class)
public interface MainComponent {
public DaoSession getDaoSession();
public MainRepositoryManager getMainRepositoryManager();
}
|
MainModule部分代码:
public class
MainModule {
@Provides
@PerApplication
public MainRepositoryManager provideRepositoryManager
(@Named("live")
Retrofit retrofit, DaoSession daoSession) {
return new MainRepositoryManager
(retrofit, daoSession);
}
@Provides
@Named("live")
@PerApplication
public Retrofit provideRetrofit(@Named("live")
OkHttpClient okHttpClient,@Nullable Gson gson){
Retrofit.Builder builder=new Retrofit.Builder().
baseUrl(LiveUtil.BASE_URL).
addCallAdapterFactory(RxJava2CallAdapterFactory.create())
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create(gson)).
client(okHttpClient);
return builder.build();
}
@Provides
@Named("live")
@PerApplication
public OkHttpClient provideOkHttpClient(@Named("live")
LiveInterceptor
interceptor){
OkHttpClient.Builder builder=new OkHttpClient.Builder();
builder.connectTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS).readTimeout
(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
builder.addInterceptor(interceptor);
return builder.build();
}
@Provides
@Named("live")
@PerApplication
public LiveInterceptor provideNewsInterceptor(){
return new LiveInterceptor();
}
}
|
难点
在项目中使用组件化,可能会遇到很多问题,下面将问题罗列如下:
资源命名冲突
官方说法是在每个 module 的 build.gradle 文件中配置资源文件名前缀。
这种方法缺点就是,所有的资源名必须要以指定的字符串(moudle_prefix)做前缀,否则会异常报错,而且这方法只限定xml里面的资源,对图片资源并不起作用,所以图片资源仍然需要手动去修改资源名。所以不是很推荐使用这种方法来解决资源名冲突。所以只能自己注意点,在创建资源的时候,尽量不让其重复。例如:
| resourcePrefix
"moudle_prefix" |
butterKnife使用问题
虽然 Butterknife 支持在 lib 中使用,但是条件是用 R2 代替 R ,在组件模式和集成模式的切换中,R2<->R
之间的切换是无法完成转换的,切换一次要改动全身,是非常麻烦的!所以不推荐在组件化中使用 Butterknife。
library重复依赖问题
相信这个问题,大家在平时的开发中都会遇到,所以我们需要将多余的包给排除出去。可以参考如下的配置:
dependencies
{
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.
espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2',
{
exclude group: 'com.android.support', module:
'support-annotations'
})
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.appcompatV7)
{
exclude module: "support-v4"
exclude module: "support-annotations"
}
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.recycleview
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.design
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.support_v4)
{
exclude module: "support-annotations"
}
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.annotations
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.butterknife)
{
exclude module: 'support-annotations'
}
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.rxjava2
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.rxjava2_android)
{
exclude module: "rxjava"
}
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.rxlifecycle2)
{
exclude module: 'rxjava'
exclude module: 'jsr305'
}
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.rxlifecycle2
_components)
{
exclude module: 'support-v4'
exclude module: 'appcompat-v7'
exclude module: 'support-annotations'
exclude module: 'rxjava'
exclude module: 'rxandroid'
exclude module: 'rxlifecycle'
}
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.retrofit)
{
exclude module: 'okhttp'
exclude module: 'okio'
}
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.
retrofit_converter_gson) {
exclude module: 'gson'
exclude module: 'okhttp'
exclude module: 'okio'
exclude module: 'retrofit'
}
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.
retrofit_adapter_rxjava2) {
exclude module: 'rxjava'
exclude module: 'okhttp'
exclude module: 'retrofit'
exclude module: 'okio'
}
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.greenDao
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.okhttp3
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.gson
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.glide
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.eventBus
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.dagger2
compile(rootProject.ext.dependencies.rxpermission)
{
exclude module: 'rxjava'
}
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.retrofit_
;converter_scalars
annotationProcessor rootProject.ext.
dependencies.dagger2_compiler
annotationProcessor rootProject.ext.
dependencies.butterknife_compiler
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.butterknife
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.transformations
compile rootProject.ext.dependencies.arouter_api
}
|
附:项目实例
聊天模块
优秀项目参考:
MVPArms
https://github.com/JessYanCoding/MVPArms
全民直播
https://github.com/jenly1314/KingTV
音乐项目
https://github.com/hefuyicoder/ListenerMusicPlayer
https://github.com/aa112901/remusic
大象:PHPHub客户端
https://github.com/Freelander/Elephant
MvpApp
https://github.com/Rukey7/MvpApp
CloudReader
https://github.com/youlookwhat/CloudReader
|