|
今天,我着重讲解下如下三个内容:
- measure过程
- WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT属性的原理说明
- xml布局文件解析成View树的流程分析。
希望对大家能有帮助。- - 分析版本基于Android 2.3 。
1、WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
初入Android殿堂的同学们,对这三个属性一定又爱又恨。爱的是使用起来挺爽地---照葫芦画瓢即可,恨的
却是时常混淆这几个属性地意义,需要三思而后行。在带着大家重温下这几个属性的用法吧(希望我没有啰嗦)。
这三个属性都用来适应视图的水平或垂直大小,一个以视图的内容或尺寸为基础的布局比精确地指定视图范围
更加方便。
① fill_parent
设置一个视图的布局为fill_parent将强制性地使视图扩展至父元素大小。
② match_parent
Android 中match_parent和fill_parent意思一样,但match_parent更贴切,于是从2.2开始两个词都可以
用,但2.3版本后建议使用match_parent。
③ wrap_content
自适应大小,强制性地使视图扩展以便显示其全部内容。以TextView和ImageView控件为例,设置为
wrap_content将完整显示其内部的文本和图像。布局元素将根据内容更改大小。
可不要重复造轮子,以上摘自<<Android fill_parent、wrap_content和match_parent的区别>>。
当然,我们可以设置View的确切宽高,而不是由以上属性指定。
01.android:layout_weight="wrap_content" //自适应大小
02.android:layout_weight="match_parent" //与父视图等高
03.android:layout_weight="fill_parent" //与父视图等高
04.android:layout_weight="100dip" //精确设置高度值为 100dip |
接下来,我们需要转换下视角,看看ViewGroup.LayoutParams类及其派生类。
2、ViewGroup.LayoutParams类及其派生类
2.1、 ViewGroup.LayoutParams类说明
Android API中如下介绍:
LayoutParams are used by views to tell
their parents how they want to be laid out.
意思大概是说: View通过LayoutParams类告诉其父视图它想要地大小(即,长度和宽度)。
因此,每个View都包含一个ViewGroup.LayoutParams类或者其派生类,View类依赖于ViewGroup.LayoutParams。
路径:frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\View.java
01.public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback, AccessibilityEventSource {
02. ...
03. /**
04. * The layout parameters associated with this view and used by the parent
05. * {@link android.view.ViewGroup} to determine how this view should be
06. * laid out.
07. * {@hide}
08. */
09. //该View拥有的 LayoutParams属性,父试图添加该View时,会为其赋值,特别注意,其类型为ViewGroup.LayoutParams。
10. protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams mLayoutParams;
11. ...
12.} |
2.2、 ViewGroup.LayoutParams源码分析
路径位于:frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\ViewGroup.java
01.public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
02. ...
03. public static class LayoutParams {
04. /**
05. * Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
06. * FILL_PARENT means that the view wants to be as big as its parent,
07. * minus the parent's padding, if any. This value is deprecated
08. * starting in API Level 8 and replaced by {@link #MATCH_PARENT}.
09. */
10. @Deprecated
11. public static final int FILL_PARENT = -1; // 注意值为-1,Android2.2版本不建议使用
12. /**
13. * Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
14. * MATCH_PARENT means that the view wants to be as big as its parent,
15. * minus the parent's padding, if any. Introduced in API Level 8.
16. */
17. public static final int MATCH_PARENT = -1; // 注意值为-1
18. /**
19. * Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
20. * WRAP_CONTENT means that the view wants to be just large enough to fit
21. * its own internal content, taking its own padding into account.
22. */
23. public static final int WRAP_CONTENT = -2; // 注意值为-2
24. /**
25. * Information about how wide the view wants to be. Can be one of the
26. * constants FILL_PARENT (replaced by MATCH_PARENT ,
27. * in API Level 8) or WRAP_CONTENT. or an exact size.
28. */
29. public int width; //该View的宽度,可以为WRAP_CONTENT/MATCH_PARENT 或者一个具体值
30. /**
31. * Information about how tall the view wants to be. Can be one of the
32. * constants FILL_PARENT (replaced by MATCH_PARENT ,
33. * in API Level 8) or WRAP_CONTENT. or an exact size.
34. */
35. public int height; //该View的高度,可以为WRAP_CONTENT/MATCH_PARENT 或者一个具体值
36. /**
37. * Used to animate layouts.
38. */
39. public LayoutAnimationController.AnimationParameters layoutAnimationParameters;
40. /**
41. * Creates a new set of layout parameters. The values are extracted from
42. * the supplied attributes set and context. The XML attributes mapped
43. * to this set of layout parameters are:、
44. */
45. public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
46. TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout);
47. setBaseAttributes(a,
48. R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_width,
49. R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_height);
50. a.recycle();
51. }
52.
53. /**
54. * Creates a new set of layout parameters with the specified width
55. * and height.
56. */
57. public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
58. this.width = width;
59. this.height = height;
60. }
61. /**
62. * Copy constructor. Clones the width and height values of the source.
63. *
64. * @param source The layout params to copy from.
65. */
66. public LayoutParams(LayoutParams source) {
67. this.width = source.width;
68. this.height = source.height;
69. }
70. /**
71. * Used internally by MarginLayoutParams.
72. * @hide
73. */
74. LayoutParams() {
75. }
76. /**
77. * Extracts the layout parameters from the supplied attributes.
78. *
79. * @param a the style attributes to extract the parameters from
80. * @param widthAttr the identifier of the width attribute
81. * @param heightAttr the identifier of the height attribute
82. */
83. protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
84. width = a.getLayoutDimension(widthAttr, "layout_width");
85. height = a.getLayoutDimension(heightAttr, "layout_height");
86. }
87.} |
我们发现FILL_PARENT/MATCH_PARENT值为 -1 ,WRAP_CONETENT值为-2,是不是有点诧异?
将值
设置为负值的目的是为了区别View的具体值(an exact size)
总是大于0的。
ViewGroup子类可以实现自定义LayoutParams,自定义LayoutParams提供了更好地扩展性,例如LinearLayout
就有LinearLayout. LayoutParams自定义类(见下文)。整个LayoutParams类家族还是挺复杂的。
ViewGroup.LayoutParams及其常用派生类的类图(部分类图)如下:
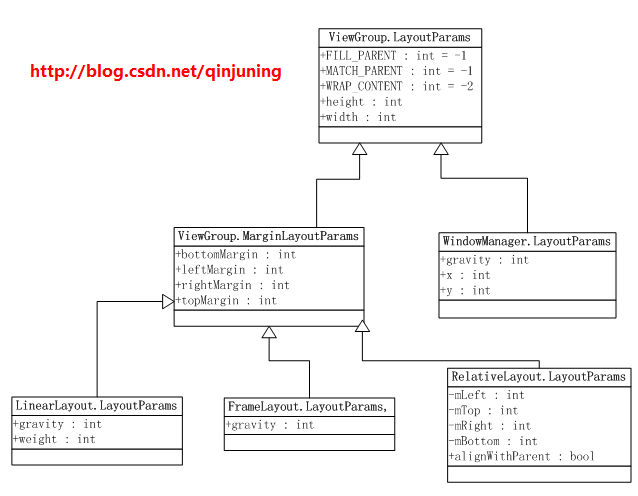
该类图是在太庞大了,大家有兴趣的去看看Android API吧。
前面我们说过,每个View都包含一个ViewGroup.LayoutParams类或者其派生类,下面我们的疑问是Android框架
中时如何为View设置其LayoutParams属性的。
有两种方法会设置View的LayoutParams属性:
1、 直接添加子View时,常见于如下几种方法:ViewGroup.java
01.//Adds a child view.
02.void addView(View child, int index)
03.//Adds a child view with this ViewGroup's default layout parameters
04.//and the specified width and height.
05.void addView(View child, int width, int height)
06.//Adds a child view with the specified layout parameters.
07.void addView(View child, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) |
三个重载方法的区别只是添加View时构造LayoutParams对象的方式不同而已,稍后我们探寻一下它们的源码。
2、 通过xml布局文件指定某个View的属性为:android:layout_heigth=””以及android:layout_weight=””
时。
总的来说,这两种方式都会设定View的LayoutParams属性值----指定的或者Default值。
方式1流程分析:
直接添加子View时,比较容易理解,我们先来看看这种方式设置LayoutParams的过程:
路径:\frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\ViewGroup.java
01.public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
02. ...
03. /**
04. * Adds a child view. If no layout parameters are already set on the child, the
05. * default parameters for this ViewGroup are set on the child.
06. *
07. * @param child the child view to add
08. *
09. * @see #generateDefaultLayoutParams()
10. */
11. public void addView(View child) {
12. addView(child, -1);
13. }
14. /**
15. * Adds a child view. If no layout parameters are already set on the child, the
16. * default parameters for this ViewGroup are set on the child.
17. *
18. * @param child the child view to add
19. * @param index the position at which to add the child
20. *
21. * @see #generateDefaultLayoutParams()
22. */
23. public void addView(View child, int index) {
24. LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
25. if (params == null) {
26. params = generateDefaultLayoutParams(); //返回默认地LayoutParams类,作为该View的属性值
27. if (params == null) {//如果不能获取到LayoutParams对象,则抛出异常。
28. throw new IllegalArgumentException("generateDefaultLayoutParams() cannot return null");
29. }
30. }
31. addView(child, index, params);
32. }
33. /**
34. * Adds a child view with this ViewGroup's default layout parameters and the
35. * specified width and height.
36. *
37. * @param child the child view to add
38. */
39. public void addView(View child, int width, int height) {
40. //返回默认地LayoutParams类,作为该View的属性值
41. final LayoutParams params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();
42. params.width = width; //重新设置width值
43. params.height = height; //重新设置height值
44. addView(child, -1, params); //这儿,我们有指定width、height的大小了。
45. }
46. /**
47. * Adds a child view with the specified layout parameters.
48. *
49. * @param child the child view to add
50. * @param params the layout parameters to set on the child
51. */
52. public void addView(View child, LayoutParams params) {
53. addView(child, -1, params);
54. }
55. /**
56. * Adds a child view with the specified layout parameters.
57. *
58. * @param child the child view to add
59. * @param index the position at which to add the child
60. * @param params the layout parameters to set on the child
61. */
62. public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params) {
63. ...
64. // addViewInner() will call child.requestLayout() when setting the new LayoutParams
65. // therefore, we call requestLayout() on ourselves before, so that the child's request
66. // will be blocked at our level
67. requestLayout();
68. invalidate();
69. addViewInner(child, index, params, false);
70. }
71. /**
72. * Returns a set of default layout parameters. These parameters are requested
73. * when the View passed to {@link #addView(View)} has no layout parameters
74. * already set. If null is returned, an exception is thrown from addView.
75. *
76. * @return a set of default layout parameters or null
77. */
78. protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
79. //width 为 WRAP_CONTENT大小 , height 为WRAP_CONTENT
80. //ViewGroup的子类可以重写该方法,达到其特定要求。稍后会以LinearLayout类为例说明。
81. return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
82. }
83. private void addViewInner(View child, int index, LayoutParams params,
84. boolean preventRequestLayout) {
85.
86. if (!checkLayoutParams(params)) { //params对象是否为null
87. params = generateLayoutParams(params); //如果params对象是为null,重新构造个LayoutParams对象
88. }
89. //preventRequestLayout值为false
90. if (preventRequestLayout) {
91. child.mLayoutParams = params; //为View的mLayoutParams属性赋值
92. } else {
93. child.setLayoutParams(params);//为View的mLayoutParams属性赋值,但会调用requestLayout()请求重新布局
94. }
95. //if else 语句会设置View为mLayoutParams属性赋值
96. ...
97. }
98. ...
99.} |
主要功能就是在添加子View时为其构建了一个LayoutParams对象。但更重要的是,ViewGroup的子类可以重载上面的几个方法,返回特定的LayoutParams对象,例如:对于LinearLayout而言,则是LinearLayout.LayoutParams对象。这么做地目的是,能在其他需要它的地方,可以将其强制转换成LinearLayout.LayoutParams对象。
LinearLayout重写函数地实现为:
01.public class LinearLayout extends ViewGroup {
02. ...
03. @Override
04. public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
05. return new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
06. }
07. @Override
08. protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
09. //该LinearLayout是水平方向还是垂直方向
10. if (mOrientation == HORIZONTAL) {
11. return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
12. } else if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
13. return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
14. }
15. return null;
16. }
17. @Override
18. protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
19. return new LayoutParams(p);
20. }
21. /**
22. * Per-child layout information associated with ViewLinearLayout.
23. *
24. * @attr ref android.R.styleable#LinearLayout_Layout_layout_weight
25. * @attr ref android.R.styleable#LinearLayout_Layout_layout_gravity
26. */ //自定义的LayoutParams类
27. public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
28. /**
29. * Indicates how much of the extra space in the LinearLayout will be
30. * allocated to the view associated with these LayoutParams. Specify
31. * 0 if the view should not be stretched. Otherwise the extra pixels
32. * will be pro-rated among all views whose weight is greater than 0.
33. */
34. @ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "layout")
35. public float weight; // 见于属性,android:layout_weight="" ;
36. /**
37. * Gravity for the view associated with these LayoutParams.
38. *
39. * @see android.view.Gravity
40. */
41. public int gravity = -1; // 见于属性, android:layout_gravity="" ;
42. /**
43. * {@inheritDoc}
44. */
45. public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
46. super(c, attrs);
47. TypedArray a =c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout);
48. weight = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_weight, 0);
49. gravity = a.getInt(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_gravity, -1);
50.
51. a.recycle();
52. }
53. /**
54. * {@inheritDoc}
55. */
56. public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
57. super(width, height);
58. weight = 0;
59. }
60. /**
61. * Creates a new set of layout parameters with the specified width, height
62. * and weight.
63. *
64. * @param width the width, either {@link #MATCH_PARENT},
65. * {@link #WRAP_CONTENT} or a fixed size in pixels
66. * @param height the height, either {@link #MATCH_PARENT},
67. * {@link #WRAP_CONTENT} or a fixed size in pixels
68. * @param weight the weight
69. */
70. public LayoutParams(int width, int height, float weight) {
71. super(width, height);
72. this.weight = weight;
73. }
74. public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
75. super(p);
76. }
77. public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
78. super(source);
79. }
80. }
81. ...
82.} |
LinearLayout.LayoutParams类继承至ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams类,添加了对android:layout_weight以及
android:layout_gravity这两个属性的获取和保存。而且它的重写函数返回的都是LinearLayout.LayoutParams类型。这样,我们可以再对子View进行其他操作时,可以将将其强制转换成LinearLayout.LayoutParams对象进行使用。
例如,LinearLayout进行measure过程,使用了LinearLayout.LayoutParam对象,有如下代码:
01.public class LinearLayout extends ViewGroup {
02. ...
03. @Override //onMeasure方法。
04. protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
05. //判断是垂直方向还是水平方向,这儿我们假设是VERTICAL垂直方向,
06. if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
07. measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
08. } else {
09. measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
10. }
11. }
12. /**
13. * Measures the children when the orientation of this LinearLayout is set
14. * to {@link #VERTICAL}.
15. *
16. * @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent.
17. * @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent.
18. *
19. * @see #getOrientation()
20. * @see #setOrientation(int)
21. * @see #onMeasure(int, int)
22. */
23. void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
24. mTotalLength = 0;
25. ...
26. // See how tall everyone is. Also remember max width.
27. for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
28. final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i); //获得索引处为i的子VIew
29. ...
30. //注意,我们将类型为 ViewGroup.LayoutParams的实例对象强制转换为了LinearLayout.LayoutParams,
31. //即父对象转换为了子对象,能这样做的原因就是LinearLayout的所有子View的LayoutParams类型都为
32. //LinearLayout.LayoutParams
33. LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
34. ...
35. }
36. ...
37.} |
超类ViewGroup.LayoutParams强制转换为了子类LinearLayout.LayoutParams,因为LinearLayout的每个”直接“子View的LayoutParams属性都是LinearLayout.LayoutParams类型,因此可以安全转换。
PS : Android 2.3源码Launcher2中也实现了自定义的LayoutParams类,在IDLE界面的每个View至少包含如下
信息:所在X方向的单元格索引和高度、所在Y方向的单元格索引和高度等。
路径: packages\apps\Launcher2\src\com\android\launcher2\CellLayout.java
01.public class CellLayout extends ViewGroup {
02. ...
03. public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
04. /**
05. * Horizontal location of the item in the grid.
06. */
07. public int cellX; //X方向的单元格索引
08. /**
09. * Vertical location of the item in the grid.
10. */
11. public int cellY; //Y方向的单元格索引
12. /**
13. * Number of cells spanned horizontally by the item.
14. */
15. public int cellHSpan; //水平方向所占高度
16. /**
17. * Number of cells spanned vertically by the item.
18. */
19. public int cellVSpan; //垂直方向所占高度
20. ...
21. public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
22. super(c, attrs);
23. cellHSpan = 1; //默认为高度 1
24. cellVSpan = 1;
25. }
26.
27. public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
28. super(source); //默认为高度 1
29. cellHSpan = 1;
30. cellVSpan = 1;
31. }
32.
33. public LayoutParams(int cellX, int cellY, int cellHSpan, int cellVSpan) {
34. super(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
35. this.cellX = cellX;
36. this.cellY = cellY;
37. this.cellHSpan = cellHSpan;
38. this.cellVSpan = cellVSpan;
39. }
40. ...
41. }
42. ...
43.} |
对该自定义CellLayout.LayoutParams类的使用可以参考LinearLayout.LayoutParams类,我也不再赘述了。
方法2流程分析:
使用属性android:layout_heigth=””以及android:layout_weight=””
时,为某个View设置LayoutParams值。
其实这种赋值方法其实也如同前面那种,只不过它需要一个前期孵化过程---需要利用XML解析将布局文件解析成一个完整的View树,可别小看它了,所有Xxx.xml的布局文件都需要解析成一个完整的View树。下面,我们就来仔细走这个过程,重点关注如下两个方面
①、xml布局是如何解析成View树的 ;
②、android:layout_heigth=””和android:layout_weight=””的解析。
PS: 一直以来,我都想当然android:layout_heigth以及android:layout_weight这两个属性的解析过程是在View.java内部完成的,但当我真正去找寻时,却一直没有在View.java类或者ViewGroup.java类找到。直到一位网友的一次提问,才发现它们的藏身之地。
3、布局文件解析流程分析
解析布局文件时,使用的类为LayoutInflater。 关于该类的使用请参考如下博客:
<android中LayoutInflater的使用 >>
主要有如下API方法:
public View inflate (XmlPullParser parser,
ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
public View inflate (int resource, ViewGroup
root)
public View inflate (int resource, ViewGroup
root, boolean attachToRoot)
这三个类主要迷惑之处在于地三个参数attachToRoot,即是否将该View树添加到root中去。具体可看这篇博客:
<<关于inflate的第3个参数>>
当然还有LayoutInflater的inflate()的其他重载方法,大家可以自行了解下。
我利用下面的例子给大家走走这个流程 :
01.public class MainActivity extends Activity {
02. /** Called when the activity is first created. */
03. @Override
04. public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
05. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
06. //1、该方法最终也会调用到 LayoutInflater的inflate()方法中去解析。
07. setContentView(R.layout.main);
08.
09. //2、使用常见的API方法去解析xml布局文件,
10. LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater)getSystemService();
11. View root = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.main, null);
12. }
13.} |
Step 1、获得LayoutInflater的引用。
路径:\frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ContextImpl.java
01./**
02. * Common implementation of Context API, which provides the base
03. * context object for Activity and other application components.
04. */
05.class ContextImpl extends Context {
06. if (WINDOW_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
07. return WindowManagerImpl.getDefault();
08. } else if (LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
09. synchronized (mSync) {
10. LayoutInflater inflater = mLayoutInflater;
11. //是否已经赋值,如果是,直接返回引用
12. if (inflater != null) {
13. return inflater;
14. }
15. //返回一个LayoutInflater对象,getOuterContext()指的是我们的Activity、Service或者Application引用
16. mLayoutInflater = inflater = PolicyManager.makeNewLayoutInflater(getOuterContext());
17. return inflater;
18. }
19. } else if (ACTIVITY_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
20. return getActivityManager();
21. }...
22.} |
继续去PolicyManager查询对应函数,看看内部实现。
路径:frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\policy\PolicyManager.java
01.public final class PolicyManager {
02. private static final String POLICY_IMPL_CLASS_NAME = "com.android.internal.policy.impl.Policy";
03. private static final IPolicy sPolicy; // 这可不是Binder机制额,这只是是一个接口,别想多啦
04. static {
05. // Pull in the actual implementation of the policy at run-time
06. try {
07. Class policyClass = Class.forName(POLICY_IMPL_CLASS_NAME);
08. sPolicy = (IPolicy)policyClass.newInstance();
09. }
10. ...
11. }
12. ...
13. public static LayoutInflater makeNewLayoutInflater(Context context) {
14. return sPolicy.makeNewLayoutInflater(context); //继续去实现类中去查找
15. }
16.} |
IPolicy接口的实现对为Policy类。路径:/frameworks/base/policy/src/com/android/internal/policy/impl/Policy.java
01.//Simple implementation of the policy interface that spawns the right
02.//set of objects
03.public class Policy implements IPolicy{
04. ...
05. public PhoneLayoutInflater makeNewLayoutInflater(Context context) {
06. //实际上返回的是PhoneLayoutInflater类。
07. return new PhoneLayoutInflater(context);
08. }
09.}
10.//PhoneLayoutInflater继承至LayoutInflater类
11.public class PhoneLayoutInflater extends LayoutInflater {
12. ...
13. /**
14. * Instead of instantiating directly, you should retrieve an instance
15. * through {@link Context#getSystemService}
16. *
17. * @param context The Context in which in which to find resources and other
18. * application-specific things.
19. *
20. * @see Context#getSystemService
21. */
22. public PhoneLayoutInflater(Context context) {
23. super(context);
24. }
25. ...
26.} |
LayoutInflater是个抽象类,实际上我们返回的是PhoneLayoutInflater类,但解析过程的操作基本上是在
LayoutInflater中完成地。
Step 2、调用inflate()方法去解析布局文件。
01.public abstract class LayoutInflater {
02. ...
03. public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root) {
04. //继续看下个函数,注意root为null
05. return inflate(resource, root, root != null);
06. }
07.
08. public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
09. //获取一个XmlResourceParser来解析XML文件---布局文件。
10. //XmlResourceParser类以及xml是如何解析的,大家自己有兴趣找找。
11. XmlResourceParser parser = getContext().getResources().getLayout(resource);
12. try {
13. return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
14. } finally {
15. parser.close();
16. }
17. }
18.}
19./**
20. * The XML parsing interface returned for an XML resource. This is a standard
21. * XmlPullParser interface, as well as an extended AttributeSet interface and
22. * an additional close() method on this interface for the client to indicate
23. * when it is done reading the resource.
24. */
25.public interface XmlResourceParser extends XmlPullParser, AttributeSet {
26. /**
27. * Close this interface to the resource. Calls on the interface are no
28. * longer value after this call.
29. */
30. public void close();
31.} |
我们获得了一个当前应用程序环境的XmlResourceParser对象,该对象的主要作用就是来解析xml布局文件的。XmlResourceParser类是个接口类,
Step 3 、真正地开始解析工作 。
01.public abstract class LayoutInflater {
02. ...
03. /**
04. * Inflate a new view hierarchy from the specified XML node. Throws
05. * {@link InflateException} if there is an error.
06. */
07. //我们传递过来的参数如下: root 为null , attachToRoot为false 。
08. public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
09. synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
10. final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
11. Context lastContext = (Context)mConstructorArgs[0];
12. mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext; //该mConstructorArgs属性最后会作为参数传递给View的构造函数
13. View result = root; //根View
14.
15. try {
16. // Look for the root node.
17. int type;
18. while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
19. type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
20. // Empty
21. }
22. ...
23. final String name = parser.getName(); //节点名,即API中的控件或者自定义View完整限定名。
24. if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { // 处理标签
25. if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
26. throw new InflateException(" can be used only with a valid "
27. + "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
28. }
29. //将标签的View树添加至root中,该函数稍后讲到。
30. rInflate(parser, root, attrs);
31. } else {
32. // Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
33. //创建该xml布局文件所对应的根View。
34. View temp = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
35.
36. ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
37.
38. if (root != null) {
39. // Create layout params that match root, if supplied
40. //根据AttributeSet属性获得一个LayoutParams实例,记住调用者为root。
41. params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
42. if (!attachToRoot) { //重新设置temp的LayoutParams
43. // Set the layout params for temp if we are not
44. // attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
45. temp.setLayoutParams(params);
46. }
47. }
48. // Inflate all children under temp
49. //添加所有其子节点,即添加所有字View
50. rInflate(parser, temp, attrs);
51.
52. // We are supposed to attach all the views we found (int temp)
53. // to root. Do that now.
54. if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
55. root.addView(temp, params);
56. }
57. // Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the
58. // top view found in xml.
59. if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
60. result = temp;
61. }
62. }
63. }
64. ...
65. return result;
66. }
67. }
68.
69. /*
70. * default visibility so the BridgeInflater can override it.
71. */
72. View createViewFromTag(String name, AttributeSet attrs) {
73. //节点是否为View,如果是将其重新赋值,形如
74. if (name.equals("view")) {
75. name = attrs.getAttributeValue(null, "class");
76. }
77. try {
78. View view = (mFactory == null) ? null : mFactory.onCreateView(name,
79. mContext, attrs); //没有设置工厂方法
80.
81. if (view == null) {
82. //通过这个判断是Android API的View,还是自定义View
83. if (-1 == name.indexOf('.')) {
84. view = onCreateView(name, attrs); //创建Android API的View实例
85. } else {
86. view = createView(name, null, attrs);//创建一个自定义View实例
87. }
88. }
89. return view;
90. }
91. ...
92. }
93. //获得具体视图的实例对象
94. public final View createView(String name, String prefix, AttributeSet attrs) {
95. Constructor constructor = sConstructorMap.get(name);
96. Class clazz = null;
97. //以下功能主要是获取如下三个类对象:
98. //1、类加载器 ClassLoader
99. //2、Class对象
100. //3、类的构造方法句柄 Constructor
101. try {
102. if (constructor == null) {
103. // Class not found in the cache, see if it's real, and try to add it
104. clazz = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name);
105. ...
106. constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature);
107. sConstructorMap.put(name, constructor);
108. } else {
109. // If we have a filter, apply it to cached constructor
110. if (mFilter != null) {
111. ...
112. }
113. }
114. //传递参数获得该View实例对象
115. Object[] args = mConstructorArgs;
116. args[1] = attrs;
117. return (View) constructor.newInstance(args);
118. }
119. ...
120. }
121.
122.} |
这段代码的作用是获取xml布局文件的root View,做了如下两件事情
1、获取xml布局的View实例,通过createViewFromTag()方法获取,该方法会判断节点名是API
控件
还是自定义控件,继而调用合适的方法去实例化View。
2、判断root以及attachToRoot参数,重新设置root View值以及temp变量的LayoutParams值。
如果仔细看着段代码,不知大家心里有没有疑惑:当root为null时,我们的temp变量的LayoutParams值是为
null的,即它不会被赋值?有个View的LayoutParams值为空,那么,在系统中不会报异常吗?见下面部分
代码:
01.//我们传递过来的参数如下: root 为null , attachToRoot为false 。
02.public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
03. synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
04. ...
05. try {
06.
07. ...
08. if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { // 处理标签
09. ...
10. } else {
11. // Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
12. //创建该xml布局文件所对应的根View。
13. View temp = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
14. ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
15.
16. //注意!!! root为null时,temp变量的LayoutParams属性不会被赋值的。
17. if (root != null) {
18. // Create layout params that match root, if supplied
19. //根据AttributeSet属性获得一个LayoutParams实例,记住调用者为root。
20. params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
21. if (!attachToRoot) { //重新设置temp的LayoutParams
22. // Set the layout params for temp if we are not
23. // attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
24. temp.setLayoutParams(params);
25. }
26. }
27. ...
28. }
29. }
30. ...
31. }
32.} |
关于这个问题的详细答案,我会在后面讲到。这儿我简单说下,任何View树的顶层View被添加至窗口时,一般调用WindowManager.addView()添加至窗口时,在这个方法中去做进一步处理。即使,LayoutParams值为空,UI框架每次measure()时都忽略该View的LayoutParams值,而是直接传递MeasureSpec值至View树。
接下来,我们关注另外一个函数,rInflate(),该方法会递归调用每个View下的子节点,以当前View作为根View形成一个View树。
01./**
02. * Recursive method used to descend down the xml hierarchy and instantiate
03. * views, instantiate their children, and then call onFinishInflate().
04. */
05.//递归调用每个字节点
06.private void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs)
07. throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
08.
09. final int depth = parser.getDepth();
10. int type;
11.
12. while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
13. parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
14.
15. if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
16. continue;
17. }
18. final String name = parser.getName();
19.
20. if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) { //处理标签
21. parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
22. } else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) { //处理标签
23. if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
24. throw new InflateException(" cannot be the root element");
25. }
26. parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs);//解析节点
27. } else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { //处理标签
28. throw new InflateException(" must be the root element");
29. } else {
30. //根据节点名构建一个View实例对象
31. final View view = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
32. final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
33. //调用generateLayoutParams()方法返回一个LayoutParams实例对象,
34. final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
35. rInflate(parser, view, attrs); //继续递归调用
36. viewGroup.addView(view, params); //OK,将该View以特定LayoutParams值添加至父View中
37. }
38. }
39. parent.onFinishInflate(); //完成了解析过程,通知....
40.} |
值得注意的是,每次addView前都调用了viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs)去构建一个LayoutParams
实例,然后在addView()方法中为其赋值。参见如下代码:ViewGroup.java
01.public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
02. ...
03.
04. public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
05. return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
06. }
07. public static class LayoutParams {
08. ... //会调用这个构造函数
09. public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
10. TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout);
11. setBaseAttributes(a,
12. R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_width,
13. R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_height);
14. a.recycle();
15. }
16. protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
17. width = a.getLayoutDimension(widthAttr, "layout_width");
18. height = a.getLayoutDimension(heightAttr, "layout_height");
19. }
20.
21.} |
好吧 ~~ 我们还是探寻根底,去TypeArray类的getLayoutDimension()看看。
路径:/frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/TypedArray.java
01.public class TypedArray {
02. ...
03. /**
04. * Special version of {@link #getDimensionPixelSize} for retrieving
05. * {@link android.view.ViewGroup}'s layout_width and layout_height
06. * attributes. This is only here for performance reasons; applications
07. * should use {@link #getDimensionPixelSize}.
08. *
09. * @param index Index of the attribute to retrieve.
10. * @param name Textual name of attribute for error reporting.
11. *
12. * @return Attribute dimension value multiplied by the appropriate
13. * metric and truncated to integer pixels.
14. */
15. public int getLayoutDimension(int index, String name) {
16. index *= AssetManager.STYLE_NUM_ENTRIES;
17. final int[] data = mData;
18. //获得属性对应的标识符 , Identifies,目前还没有仔细研究相关类。
19. final int type = data[index+AssetManager.STYLE_TYPE];
20. if (type >= TypedValue.TYPE_FIRST_INT
21. && type <= TypedValue.TYPE_LAST_INT) {
22. return data[index+AssetManager.STYLE_DATA];
23. } else if (type == TypedValue.TYPE_DIMENSION) { //类型为dimension类型
24. return TypedValue.complexToDimensionPixelSize(
25. data[index+AssetManager.STYLE_DATA], mResources.mMetrics);
26. }
27. //没有提供layout_weight和layout_height会来到此处 ,这儿会报异常!
28. //因此布局文件中的View包括自定义View必须加上属性layout_weight和layout_height。
29. throw new RuntimeException(getPositionDescription()
30. + ": You must supply a " + name + " attribute.");
31. }
32. ...
33.} |
从上面得知, 我们将View的AttributeSet属性传递给generateLayoutParams()方法,让其构建合适地LayoutParams对象,并且初始化属性值weight和height。同时我们也得知
布局文件中的View包括自定义View必须加上属性layout_weight和layout_height,否则会报异常。
Step 3 主要做了如下事情:
首先,获得了了布局文件地root View,即布局文件中最顶层的View。
其次,通过递归调用,我们形成了整个View树以及设置了每个View的LayoutParams对象。
总结:通过对布局文件的解析流程的学习,也就是转换为View树的过程,我们明白了解析过程的个中奥妙,以及
设置ViewLayoutParams对象的过程。但是,我们这儿只是简单的浮光掠影,更深层次的内容希望大家能深入学习。
本来是准备接下去往下写的,但无奈贴出来的代码太多,文章有点长而且自己也有点凌乱了,因此决定做两篇博客发表吧。下篇内容包括如下方面:
- MeasureSpec类说明 ;
- measure过程中如何正确设置每个View的长宽 ;
- UI框架正确设置顶层View的LayoutParams对象,对Activity而言,顶层View则是DecorView,其他的皆是普通View了。
上篇文章中,我们了解了View树的转换过程以及如何设置View的LayoutParams的。本文继续沿着既定轨迹继续未完成的job。
主要知识点如下:
- MeasureSpc类说明
- measure过程详解(揭秘其细节);
- root View被添加至窗口时,UI框架是如何设置其LayoutParams值得。
在讲解measure过程前,我们非常有必要理解MeasureSpc类的使用,否则理解起来也只能算是囫囵吞枣。
1、MeasureSpc类说明
1.1 SDK 说明如下
A MeasureSpec encapsulates the layout
requirements passed from parent to child. Each MeasureSpec
represents a requirement for either the width or the
height. A MeasureSpec is comprised of a size and a mode.
即:
MeasureSpc类封装了父View传递给子View的布局(layout)要求。每个MeasureSpc实例代表宽度或者高度(只能是其一)要求。
它有三种模式:
①、UNSPECIFIED(未指定),父元素部队自元素施加任何束缚,子元素可以得到任意想要的大小;
②、EXACTLY(完全),父元素决定自元素的确切大小,子元素将被限定在给定的边界里而忽略它本身大小;
③、AT_MOST(至多),子元素至多达到指定大小的值。
常用的三个函数:
static int getMode(int measureSpec)
: 根据提供的测量值(格式)提取模式(上述三个模式之一)
static int getSize(int measureSpec)
: 根据提供的测量值(格式)提取大小值(这个大小也就是我们通常所说的大小)
static int makeMeasureSpec(int size,int
mode) : 根据提供的大小值和模式创建一个测量值(格式)
1.2 MeasureSpc类源码分析
其为View.java类的内部类,路径:\frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\View.java
01.public class View implements ... {
02. ...
03. public static class MeasureSpec {
04. private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30; //移位位数为30
05. //int类型占32位,向右移位30位,该属性表示掩码值,用来与size和mode进行"&"运算,获取对应值。
06. private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
07.
08. //向右移位30位,其值为00 + (30位0) , 即 0x0000(16进制表示)
09. public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
10. //向右移位30位,其值为01 + (30位0) , 即0x1000(16进制表示)
11. public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
12. //向右移位30位,其值为02 + (30位0) , 即0x2000(16进制表示)
13. public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
14.
15. //创建一个整形值,其高两位代表mode类型,其余30位代表长或宽的实际值。
可以是WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT或具体大小exactly size
16. public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
17. return size + mode;
18. }
19. //获取模式 ,与运算
20. public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
21. return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
22. }
23. //获取长或宽的实际值 ,与运算
24. public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
25. return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
26. }
27.
28. }
29. ...
30.} |
MeasureSpec类的处理思路是:
①、右移运算,使int 类型的高两位表示模式的实际值,其余30位表示其余30位代表长或宽的实际值----可以是
WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT或具体大小exactly
size。
②、通过掩码MODE_MASK进行与运算 “&”,取得模式(mode)以及长或宽(value)的实际值。
2、measure过程详解
2.1 measure过程深入分析
之前的一篇博文<< Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析>>,我们从”二B程序员”的角度简单
解了measure过程的调用过程。过了这么多,我们也该升级了,- - 。现在请开始从”普通程序员”角度去理解这个过程。我们重点查看measure过程中地相关方法。
我们说过,当UI框架开始绘制时,皆是从ViewRoot.java类开始绘制的。ViewRoot类简要说明:
任何显示在设备中的窗口,例如:Activity、Dialog等,都包含一个ViewRoot实例,该类主要用来与远端
WindowManagerService交互以及控制(开始/销毁)绘制。
Step 1、 开始UI绘制 , 具体绘制方法则是:
01.路径:\frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\ViewRoot.java
02.public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,View.AttachInfo.Callbacks {
03. ...
04. //mView对象指添加至窗口的root View ,对Activity窗口而言,则是DecorView对象。
05. View mView;
06.
07. //开始View绘制流程
08. private void performTraversals(){
09. ...
10. //这两个值我们在后面讨论时,在回过头来看看是怎么赋值的。现在只需要记住其值MeasureSpec.
makeMeasureSpec()构建的。
11. int childWidthMeasureSpec; //其值由MeasureSpec类构建 , makeMeasureSpec
12. int childHeightMeasureSpec;//其值由MeasureSpec类构建 , makeMeasureSpec
13.
14.
15. // Ask host how big it wants to be
16. host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
17. ...
18. }
19. ...
20.} |
这儿,我并没有说出childWidthMeasureSpec和childHeightMeasureSpec类的来由(为了避免额外地开销,等到
第三部分时我们在来攻克它,现在只需要记住其值MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec()构建的。
Step 2 、调用measure()方法去做一些前期准备
measure()方法原型定义在View.java类中,final修饰符修饰,其不能被重载:
01.public class View implements ... {
02. ...
03. /**
04. * This is called to find out how big a view should be. The parent
05. * supplies constraint information in the width and height parameters.
06. *
07. * @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the
08. * parent
09. * @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the
10. * parent
11. * @see #onMeasure(int, int)
12. */
13. public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
14. //判断是否为强制布局,即带有“FORCE_LAYOUT”标记 以及 widthMeasureSpec或heightMeasureSpec发生了改变
15. if ((mPrivateFlags & FORCE_LAYOUT) == FORCE_LAYOUT ||
16. widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec ||
17. heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec) {
18.
19. // first clears the measured dimension flag
20. //清除MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET标记 ,该标记会在onMeasure()方法后被设置
21. mPrivateFlags &= ~MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
22.
23. // measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
24. // 1、 测量该View本身的大小 ; 2 、 设置MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET标记,否则接写来会报异常。
25. onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
26.
27. // flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
28. // an exception to warn the developer
29. if ((mPrivateFlags & MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
30. throw new IllegalStateException("onMeasure() did not set the"
31. + " measured dimension by calling" + " setMeasuredDimension()");
32. }
33.
34. mPrivateFlags |= LAYOUT_REQUIRED; //下一步是layout了,添加LAYOUT_REQUIRED标记
35. }
36.
37. mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec; //保存值
38. mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec; //保存值
39. }
40. ...
41.} |
参数widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec
由父View构建,表示父View给子View的测量要求。其值地构建
会在下面步骤中详解。
measure()方法显示判断是否需要重新调用设置改View大小,即调用onMeasure()方法,然后操作两个标识符:
①、重置MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET : onMeasure()方法中,需要添加该标识符,否则,会报异常;
②、添加LAYOUT_REQUIRED : 表示需要进行layout操作。
最后,保存当前的widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec值。
Step 3 、调用onMeasure()方法去真正设置View的长宽值,其默认实现为:
01./**
02. * Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the
03. * measured height. This method is invoked by {@link #measure(int, int)} and
04. * should be overriden by subclasses to provide accurate and efficient
05. * measurement of their contents.
06. *
07. * @param widthMeasureSpec horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent.
08. * The requirements are encoded with
09. * @param heightMeasureSpec vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent.
10. * The requirements are encoded with
11. */
12. //设置该View本身地大小
13. protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
14. setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
15. getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
16. }
17.
18. /**
19. * Utility to return a default size. Uses the supplied size if the
20. * MeasureSpec imposed no contraints. Will get larger if allowed
21. * by the MeasureSpec.
22. *
23. * @param size Default size for this view
24. * @param measureSpec Constraints imposed by the parent
25. * @return The size this view should be.
26. */
27. //@param size参数一般表示设置了android:minHeight属性或者该View背景图片的大小值
28. public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
29. int result = size;
30. int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
31. int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
32.
33. //根据不同的mode值,取得宽和高的实际值。
34. switch (specMode) {
35. case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: //表示该View的大小父视图未定,设置为默认值
36. result = size;
37. break;
38. case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: //表示该View的大小由父视图指定了
39. case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
40. result = specSize;
41. break;
42. }
43. return result;
44. }
45. //获得设置了android:minHeight属性或者该View背景图片的大小值, 最为该View的参考值
46. protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
47. int suggestedMinWidth = mMinWidth; // android:minHeight
48.
49. if (mBGDrawable != null) { // 背景图片对应地Width。
50. final int bgMinWidth = mBGDrawable.getMinimumWidth();
51. if (suggestedMinWidth < bgMinWidth) {
52. suggestedMinWidth = bgMinWidth;
53. }
54. }
55.
56. return suggestedMinWidth;
57. }
58. //设置View在measure过程中宽和高
59. protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
60. mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
61. mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
62.
63. mPrivateFlags |= MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET; //设置了MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET标记
64. } |
主要功能就是根据该View属性(android:minWidth和背景图片大小)和父View对该子View的"测量要求",设置该
View的 mMeasuredWidth 和 mMeasuredHeight 值。
这儿只是一般的View类型地实现方法。一般来说,父View,也就是ViewGroup类型,都需要在重写onMeasure()
方法,遍历所有子View,设置每个子View的大小。基本思想如下:遍历所有子View,设置每个子View的大小。伪代码表示为:
01.//某个ViewGroup类型的视图
02.protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
03. //必须调用super.ononMeasure()或者直接调用setMeasuredDimension()方法设置该View大小,否则会报异常。
04. super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec , heightMeasureSpec)
05. //setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
06. // getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
07.
08. //遍历每个子View
09. for(int i = 0 ; i < getChildCount() ; i++){
10. View child = getChildAt(i);
11. //调用子View的onMeasure,设置他们的大小。childWidthMeasureSpec , childHeightMeasureSpec ?
12. child.onMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
13. }
14.} |
Step 2、Step 3 代码也比较好理解,但问题是我们示例代码中widthMeasureSpec、heightMeasureSpec是如何确定的呢?父View是如何设定其值的?
要想回答这个问题,我们看是去源代码里找找答案吧。在ViewGroup.java类中,为我们提供了三个方法,去设置每个子View的大小,基本思想也如同我们之前描述的思想:遍历所有子View,设置每个子View的大小。
主要有如下方法:
01./**
02. * Ask all of the children of this view to measure themselves, taking into
03. * account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding.
04. * We skip children that are in the GONE state The heavy lifting is done in
05. * getChildMeasureSpec.
06. */
07.//widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 表示该父View的布局要求
08.//遍历每个子View,然后调用measureChild()方法去实现每个子View大小
09.protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
10. final int size = mChildrenCount;
11. final View[] children = mChildren;
12. for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
13. final View child = children[i];
14. if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) { // 不处于 “GONE” 状态
15. measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
16. }
17. }
18.}
19.
20./**
21. * Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into
22. * account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding.
23. * The heavy lifting is done in getChildMeasureSpec.
24. *
25. * @param child The child to measure
26. * @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
27. * @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
28. */
29.//测量每个子View高宽时,清楚了该View本身的边距大小,即android:padding属性 或android:paddingLeft等属性标记
30.protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
31. int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
32. final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams(); // LayoutParams属性
33. //设置子View的childWidthMeasureSpec属性,去除了该父View的边距值 mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight
34. final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
35. mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
36. //设置子View的childHeightMeasureSpec属性,去除了该父View的边距值 mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom
37. final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
38. mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
39.
40. child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
41.} |
measureChildren()方法:遍历所有子View,调用measureChild()方法去设置该子View的属性值。
measureChild() 方法 : 获取特定子View的widthMeasureSpec、heightMeasureSpec,调用measure()方法设置子View的实际宽高值。
getChildMeasureSpec()就是获取子View的widthMeasureSpec、heightMeasureSpec值。
01./**
02. * Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to
03. * pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec
04. * for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.
05. *
06. * The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the
07. * LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results.
08. */
09.// spec参数 表示该父View本身所占的widthMeasureSpec 或 heightMeasureSpec值
10.// padding参数 表示该父View的边距大小,见于android:padding属性 或android:paddingLeft等属性标记
11.// childDimension参数 表示该子View内部LayoutParams属性的值,可以是wrap_content、match_parent、
一个精确指(an exactly size),
12.// 例如:由android:width指定等。
13.public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
14. int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec); //获得父View的mode
15. int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec); //获得父View的实际值
16.
17. int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding); //父View为子View设定的大小,减去边距值,
18.
19. int resultSize = 0; //子View对应地 size 实际值 ,由下面的逻辑条件赋值
20. int resultMode = 0; //子View对应地 mode 值 , 由下面的逻辑条件赋值
21.
22. switch (specMode) {
23. // Parent has imposed an exact size on us
24. //1、父View是EXACTLY的 !
25. case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
26. //1.1、子View的width或height是个精确值 (an exactly size)
27. if (childDimension >= 0) {
28. resultSize = childDimension; //size为精确值
29. resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY 。
30. }
31. //1.2、子View的width或height为 MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
32. else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
33. // Child wants to be our size. So be it.
34. resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
35. resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY 。
36. }
37. //1.3、子View的width或height为 WRAP_CONTENT
38. else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
39. // Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
40. // bigger than us.
41. resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
42. resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; //mode为AT_MOST 。
43. }
44. break;
45.
46. // Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
47. //2、父View是AT_MOST的 !
48. case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
49. //2.1、子View的width或height是个精确值 (an exactly size)
50. if (childDimension >= 0) {
51. // Child wants a specific size... so be it
52. resultSize = childDimension; //size为精确值
53. resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY 。
54. }
55. //2.2、子View的width或height为 MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
56. else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
57. // Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
58. // Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
59. resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
60. resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; //mode为AT_MOST
61. }
62. //2.3、子View的width或height为 WRAP_CONTENT
63. else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
64. // Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
65. // bigger than us.
66. resultSize = size; //size为父视图大小
67. resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST; //mode为AT_MOST
68. }
69. break;
70.
71. // Parent asked to see how big we want to be
72. //3、父View是UNSPECIFIED的 !
73. case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
74. //3.1、子View的width或height是个精确值 (an exactly size)
75. if (childDimension >= 0) {
76. // Child wants a specific size... let him have it
77. resultSize = childDimension; //size为精确值
78. resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; //mode为 EXACTLY
79. }
80. //3.2、子View的width或height为 MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
81. else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
82. // Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
83. // be
84. resultSize = 0; //size为0! ,其值未定
85. resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED; //mode为 UNSPECIFIED
86. }
87. //3.3、子View的width或height为 WRAP_CONTENT
88. else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
89. // Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
90. // big it should be
91. resultSize = 0; //size为0! ,其值未定
92. resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED; //mode为 UNSPECIFIED
93. }
94. break;
95. }
96. //根据上面逻辑条件获取的mode和size构建MeasureSpec对象。
97. return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
98.} |
为了便于分析,我将上面的逻辑判断语句使用列表项进行了说明.
getChildMeasureSpec()方法的主要功能如下:
根据父View的measureSpec值(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec)值以及子View的子View内部LayoutParams属性值,共同决定子View的measureSpec值的大小。主要判断条件主要为MeasureSpec的mode类型以及LayoutParams的宽高实际值(lp.width,lp.height),见于以上所贴代码中的列表项:
1、 1.1 ; 1.2 ; 1.3 ; 2、2.1等。
例如,分析列表3:假设当父View为MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED类型,即未定义时,只有当子View的width或height指定时,其mode才为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,否者该View
size为 0 ,mode为MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED时,即处于未指定状态。
由此可以得出, 每个View大小的设定都事由其父View以及该View共同决定的。但这只是一个期望的大小,每个View在测量时最终大小的设定是由setMeasuredDimension()最终决定的。因此,最终确定一个View的“测量长宽“是由以下几个方面影响:
- 父View的MeasureSpec属性;
- 子View的LayoutParams属性 ;
- setMeasuredDimension()或者其它类似设定 mMeasuredWidth 和
mMeasuredHeight 值的方法。
setMeasuredDimension()原型:
01.//设置View在measure过程中宽和高
02.protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
03. mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
04. mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
05.
06. mPrivateFlags |= MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET; //设置了MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET标记
07.} |
将上面列表项转换为表格为:
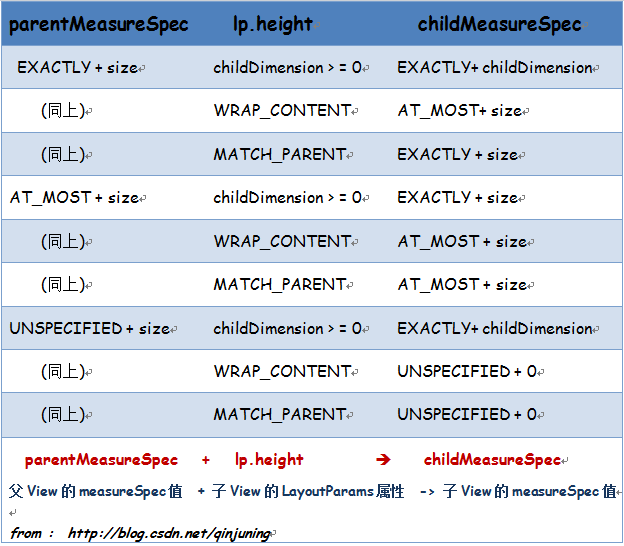
这张表格更能帮助我们分析View的MeasureSpec的确定条件关系。
为了帮助大家理解,下面我们分析某个窗口使用地xml布局文件,我们弄清楚该xml布局文件中每个View的
MeasureSpec值的组成。
01.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
02.<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
03. android:id="@+id/llayout"
04. android:orientation="vertical"
05. android:layout_width="match_parent"
06. android:layout_height="match_parent">
07.
08.
09. <TextView android:id="@+id/tv"
10. android:layout_width="match_parent"
11. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
12. android:text="@string/hello" />
13.
14.</LinearLayout> |
该布局文件共有两个View: ①、id为llayout的LinearLayout布局控件
;②、id为tv的TextView控件。
假设LinearLayout的父View对应地widthSpec和heightSpec值皆为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY类型(Activity窗口的父View为DecorView,具体原因见第三部分说明)。
对LinearLayout而言比较简单,由于 android:layout_width="match_parent",因此其width对应地widthSpec
mode值为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY , size由父视图大小指定 ; 由于android:layout_height
= "match_parent",因此其height对应地heightSpec mode值为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,size由父视图大小指定
;
对TextView而言 ,其父View为LinearLayout的widthSpec和heightSpec值皆为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY类型,由于android:layout_width="match_parent"
, 因此其width对应地widthSpec mode值为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,size由父视图大小指定
; 由于android:layout_width="wrap_content" ,
因此其height对应地widthSpec mode值为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST,size由父视图大小指定
。
我们继续窥测下LinearLayout类是如何进行measure过程的:
01. public class LinearLayout extends ViewGroup {
02....
03.@Override //onMeasure方法。
04.protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
05. //判断是垂直方向还是水平方向,这儿我们假设是VERTICAL垂直方向,
06. if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
07. measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
08. } else {
09. measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
10. }
11.}
12.//垂直方向布局
13. void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
14. mTotalLength = 0; //该LinearLayout测量子View时的总高度。
15. float totalWeight = 0; //所有子View的权重和 , android:layout_weight
16. int maxWidth = 0; //保存子View中最大width值
17. ...
18. final int count = getVirtualChildCount(); //子View的个数
19.
20. final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
21. final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
22. ...
23. // See how tall everyone is. Also remember max width.
24. for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
25. final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
26. ...
27. LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
28.
29. totalWeight += lp.weight;
30. //满足该条件地View会在该LinearLayout有剩余高度时,才真正调用measure()
31. if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
32. ...
33. } else {
34. int oldHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
35. //如果View的hight值为0,并且设置了android:layout_weight属性,重新纠正其height值为WRAP_CONTENT
36. if (lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
37. oldHeight = 0;
38. lp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
39. }
40. // Determine how big this child would like to be. If this or
41. // previous children have given a weight, then we allow it to
42. // use all available space (and we will shrink things later
43. // if needed).
44. //对每个子View调用measure()方法
45. measureChildBeforeLayout(
46. child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec,
47. totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0);
48.
49. //这三行代码做了如下两件事情:
50. //1、获得该View的measuredHeight值,每个View都会根据他们地属性正确设置值 > 0 ;
51. //2、更新mTotalLength值:取当前高度mTotalLength值与mTotalLength + childHeight 的最大值
52. // 于是对于android:layout_height="wrap_height"属性地LinearLayout控件也就知道了它的确切高度值了。
53. final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
54. final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
55. mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin +
56. lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
57. ...
58. }
59. final int margin = lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
60. final int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + margin;
61. maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, measuredWidth);
62. ...
63. }
64. //后续还有很多处理,包括继续measure()某些符合条件地子View
65. ...
66. }
67. void measureChildBeforeLayout(View child, int childIndex,
68. int widthMeasureSpec, int totalWidth, int heightMeasureSpec,
69. int totalHeight) {
70. //调用measureChildWithMargins()方法去设置子View大小
71. measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, totalWidth,
72. heightMeasureSpec, totalHeight);
73. }
74.... |
继续看看measureChildWithMargins()方法,该方法定义在ViewGroup.java内,基本流程同于measureChild()方法,但添加了对子View
Margin的处理,即:android:margin属性或者android:marginLeft等属性的处理。
measureChildWithMargins@ViewGroup.java
01./**
02. * Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into
03. * account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding
04. * and margins. The child must have MarginLayoutParams The heavy lifting is
05. * done in getChildMeasureSpec.
06. */
07.//基本流程同于measureChild()方法,但添加了对子View Margin的处理,
即:android:margin属性或者android:marginLeft等属性的处理
08.//widthUsed参数 表示该父View已经使用的宽度
09.//heightUsed参数 表示该父View已经使用的高度
10.protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
11. int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
12. int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
13. final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
14.
15. //获得子View的childWidthMeasureSpec和childHeightMeasureSpec值
16. final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
17. mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
18. + widthUsed, lp.width);
19. final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
20. mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
21. + heightUsed, lp.height);
22.
23. child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
24.}
|
measure()过程时,LinearLayout类做了如下事情 :
1、遍历每个子View,对其调用measure()方法;
2、子View measure()完成后,需要取得该子View地宽高实际值,继而做处理(例如:LinearLayout属性为android:widht="wrap_content"时,LinearLayout的实际width值则是每个子View的width值的累加值)。
2.2 WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT以及measure动机揭秘子View地宽高实际值
,即child.getMeasuredWidth()值得返回最终会是一个确定值? 难道WRAP_CONTENT(其值为-2)
、MATCH_PARENT(值为-1)或者说一个具体值(an exactly size > 0)。前面我们说过,View最终“测量”值的确定是有三个部分组成地:
①、父View的MeasureSpec属性;
②、子View的LayoutParams属性 ;
③、setMeasuredDimension()或者其它类似设定 mMeasuredWidth
和 mMeasuredHeight 值的方法。
因此,一个View必须以某种合适地方法确定它地最终大小。例如,如下自定义View:
01.//自定义View
02.public Class MyView extends View {
03.
04. //针对不同地mode值,设置本View地大小
05. protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec){
06. //获得父View传递给我们地测量需求
07. int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
08. int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
09.
10. int width = 0 ;
11. int height = 0 ;
12. //对UNSPECIFIED 则抛出异常
13. if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED || heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)
14. throw new RuntimeException("widthMode or heightMode cannot be UNSPECIFIED");
15.
16. //精确指定
17. if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
18. width = 100 ;
19. }
20. //模糊指定
21. else if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST )
22. width = 50 ;
23.
24. //精确指定
25. if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
26. height = 100 ;
27. }
28. //模糊指定
29. else if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST )
30. height = 50 ;
31.
32. setMeasuredDimension(width , height) ;
33. }
34.} |
该自定义View重写了onMeasure()方法,根据传递过来的widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec简单设置了该View的mMeasuredWidth
和 mMeasuredHeight值。
对于TextView而言,如果它地mode不是Exactly类型 , 它会根据一些属性,例如:android:textStyle、android:textSizeandroid:typeface等去确定TextView类地需要占用地长和宽。
因此,如果你地自定义View必须手动对不同mode做出处理。否则,则是mode对你而言是无效的。
Android框架中提供地一系列View/ViewGroup都需要去进行这个measure()过程地
,因为在layout()过程中,父View需要调用getMeasuredWidth()或getMeasuredHeight()去为每个子View设置他们地布局坐标,只有确定布局坐标后,才能真正地将该View
绘制(draw)出来,否则该View的layout大小为0,得不到期望效果。我们继续看看LinearLayout的layout布局过程:
01.public class LinearLayout extends ViewGroup {
02. ...
03. @Override //layout 过程
04. protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
05. //假定是垂直方向布局
06. if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
07. layoutVertical();
08. } else {
09. layoutHorizontal();
10. }
11. }
12. //对每个子View调用layout过程
13. void layoutVertical() {
14. ...
15. final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
16. ...
17. for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
18. final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
19. if (child == null) { //一般为非null
20. childTop += measureNullChild(i);
21. } else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
22. //获得子View测量时的实际宽高值,
23. final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
24. final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
25.
26. ...
27. // 封装了child.layout()方法,见如下
28. setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child),
29. childWidth, childHeight);
30. childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child);
31.
32. i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
33. }
34. }
35. }
36. //width = getMeasuredWidth() ; height = childHeight(); View的大小就是测量大小
37. private void setChildFrame(View child, int left, int top, int width, int height) {
38.
39. child.layout(left, top, left + width, top + height);
40. }
41. ...
42.} |
对一个View进行measure操作地主要目的就是为了确定该View地布局大小,见上面所示代码。但measure操作通常是耗时的,因此对自定义ViewGroup而言,我们可以自由控制measure、layout过程,如果我们知道如何layout一个View,我们可以跳过该ViewGroup地measure操作(onMeasure()方法中measure所有子View地),直接去layout
在前面一篇博客<<Android中滑屏初探 ---- scrollTo
以及 scrollBy方法使用说明>>中,我们自定义了一个 ViewGroup, 并且重写了onMeasure()和onLayout()方法去分别操作每个View。就该ViewGroup而言,我们只需要重写onLayout()操作即可,因为我们知道如何layout每个子View。如下代码所示:
01.//自定义ViewGroup , 包含了三个LinearLayout控件,存放在不同的布局位置
02.public class MultiViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
03. private void init() {
04. // 初始化3个 LinearLayout控件
05. LinearLayout oneLL = new LinearLayout(mContext);
06. oneLL.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED);
07. addView(oneLL);
08. ...
09. }
10. @Override
11. // 我们知晓每个子View的layout布局大小,因此我们不需要为每个子View进行measure()操作了。
12.// protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
13.// setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
14.// // 设置该ViewGroup的大小
15.// int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
16.// int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
17.// int childCount = getChildCount();
18.// for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
19.// View child = getChildAt(i);
20.// // 设置每个子视图的大小 , 即全屏
21.// child.measure(MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth, MultiScreenActivity.scrrenHeight);
22.// }
23. }
24.
25. // layout过程
26. @Override
27. protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
28. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
29. Log.i(TAG, "--- start onLayout --");
30. int startLeft = 0; // 每个子视图的起始布局坐标
31. int startTop = 10; // 间距设置为10px 相当于 android:marginTop= "10px"
32. int childCount = getChildCount();
33. Log.i(TAG, "--- onLayout childCount is -->" + childCount);
34. for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
35. View child = getChildAt(i);
36. child.layout(startLeft, startTop,
37. startLeft + MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth,
38. startTop + MultiScreenActivity.scrrenHeight);
39. startLeft = startLeft + MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth ; //校准每个子View的起始布局位置
40. //三个子视图的在屏幕中的分布如下 [0 , 320] / [320,640] / [640,960]
41. }
42. }
43.} |
3、root View被添加至窗口时,UI框架是如何设置其LayoutParams值
老子道德经有言:“道生一,一生二,二生三,三生万物。” UI绘制也就是个递归过程。理解其基本架构后,也就“掌握了一个中心点”了。在第一节中,我们没有说明开始UI绘制时
,没有说明mView.measure()参数地由来,参数也就是我们本节需要弄懂的“道” --- root
View的 widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec 是如何确定的。
对于如下布局文件: main.xml
01.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
02.<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
03. android:orientation="vertical"
04. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
05. android:layout_height="fill_parent"
06. >
07.<TextView
08. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
09. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
10. android:text="@string/hello"
11. />
12.</LinearLayout> |
当使用LayoutInflater类解析成View时 ,LinearLayout对象的LayoutParams参数为null
。具体原因请参考上篇博文
任何一个View被添加至窗口时,都需要利用WindowManager类去操作。例如,如下代码:
01.//显示一个悬浮窗吧 , just so so
02.public void showView()
03.{
04. //解析布局文件
05. LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater)getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
06. //rootView对应地LayoutParams属性值为null,将会在UI绘制时设定其值
07. View rootView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.main, null);
08.
09. WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager)getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
10. //设置WindowManager.LayoutParams参数值,作为该窗口的各种属性
11. WindowManager.LayoutParams winparams = WindowManager.LayoutParams();
12. // 以屏幕左上角为原点,设置x、y初始值
13. winparams.x = 0;
14. winparams.y = 0;
15.
16. //设置悬浮窗口长宽数据
17. winparams.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;;
18. winparams.height = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;;
19.
20. windowManager.addView(rootView, winparams);
21.} |
下面,我们从获得WindowManager对象引用开始,一步步观察addView()做了一些什么事情。
Step 1 、获得WindowManager对象服务 ,具体实现类在ContextImpl.java内中
路径: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
01.@Override
02.public Object getSystemService(String name) {
03. if (WINDOW_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
04. return WindowManagerImpl.getDefault();
05. }
06. ...
07.} |
WindowManager是个接口,具体返回对象则是WindowManagerImpl的单例对象。
Step 2 、 获得WindowManagerImpl的单例对象,以及部分源码分析
路径: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerImpl.java
01.public class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager{
02.
03. public static WindowManagerImpl getDefault()
04. {
05. return mWindowManager;
06. }
07. //以特定Window属性添加一个窗口
08. public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params)
09. {
10. addView(view, params, false);
11. }
12. //参数nest表示该窗口是不是一个字窗口
13. private void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, boolean nest)
14. { ...
15. final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams)params;
16.
17. ViewRoot root;
18. View panelParentView = null; //该子窗口对应地父窗口View
19.
20. synchronized (this) {
21.
22. ...//需要对传递过来地参数进行检测...
23.
24. //对每个窗口皆构建一个ViewRoot对象
25. root = new ViewRoot(view.getContext());
26. root.mAddNesting = 1;
27. //设置root View 的LayoutParams为wparams,即WindowManager.LayoutParams类型
28. view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
29. ...//对参数检测,以及拷贝原有数组...
30.
31. //将窗口对应地view、root、wparams保存在属性集合中
32. mViews[index] = view;
33. mRoots[index] = root;
34. mParams[index] = wparams;
35. }
36. // do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
37. // 调用ViewRoot对象去通知系统添加一个窗口
38. root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
39. }
40. ...
41. //这三个数组分别保存了一个窗口对应地属性
42. private View[] mViews; //root View对象 , View类型
43. private ViewRoot[] mRoots; //ViewRoot类型 , 与WMS通信
44. private WindowManager.LayoutParams[] mParams; //窗口属性
45.
46. //WindowManagerImpl实现了单例模式
47. private static WindowManagerImpl mWindowManager = new WindowManagerImpl();
48.} |
WindowManagerImpl类的三个数组集合保存了每个窗口相关属性,这样我们可以通过这些属性去操作特定的窗口(例如,可以根据View去更新/销毁该窗口)。当参数检查成功时,构建一个ViewRoot对象,并且设置设置root
View 的LayoutParams为wparams,即WindowManager.LayoutParams类型。最后调用root.setView()方法去通知系统需要创建该窗口。我们接下来往下看看ViewRoot类相关操作。
Step 3、
01.public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,View.AttachInfo.Callbacks {
02.
03. View mView; //所有窗口地root View
04. final WindowManager.LayoutParams mWindowAttributes = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
05.
06. ...
07. /**
08. * We have one child
09. */
10. public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
11. View panelParentView) {
12. synchronized (this) {
13. if (mView == null) {
14. mView = view;
15. mWindowAttributes.copyFrom(attrs); //保存WindowManager.LayoutParams属性值
16. attrs = mWindowAttributes;
17. ...
18.
19. mAdded = true;
20. int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */
21.
22. // Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
23. // manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
24. // any other events from the system.
25. requestLayout(); //请求UI开始绘制。
26. mInputChannel = new InputChannel(); //创建一个InputChannel对象,接受消息
27. try {
28. //通知WindowManagerService添加一个窗口
29. res = sWindowSession.add(mWindow, mWindowAttributes,
30. getHostVisibility(), mAttachInfo.mContentInsets,
31. mInputChannel);
32. }
33. ...
34. view.assignParent(this); //将root View的父View设置为该ViewRoot对象(实现了ViewParent接口)
35. ...
36. }
37. }
38. }
39.} |
说明:ViewRoot类继承了Handler,实现了ViewParent接口
setView()方法地主要功能如下:
- 保存相关属性值,例如:mView、mWindowAttributes等;
- 调用requestLayout()方法请求UI绘制,由于ViewRoot是个Handler对象,异步请求;
- 通知WindowManagerService添加一个窗口;
- 注册一个事件监听管道,用来监听:按键(KeyEvent)和触摸(MotionEvent)事件。
我们这儿重点关注 requestLayout()方法请求UI绘制地流程。
Step 4、异步调用请求UI绘制
01./**
02. * {@inheritDoc}
03. */
04.public void requestLayout() {
05. checkThread(); //检查是不是UI线程调用,如果不是UI线程,会报异常
06. mLayoutRequested = true; //置为真,表示需要进行measure和layout过程
07. scheduleTraversals();
08.}
09.//开始UI绘制流程
10.public void scheduleTraversals() {
11. if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
12. mTraversalScheduled = true; //防止多次调用
13. sendEmptyMessage(DO_TRAVERSAL); //异步请求UI绘制
14. }
15.}
16.@Override
17.public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
18. switch (msg.what) {
19. case DO_TRAVERSAL:
20. performTraversals(); //开始UI绘制
21. break;
22. }
23.} |
由于performTraversals()方法比较复杂,我们侧重于第一次设置root
View的widhtSpecSize以及
heightSpecSize值。
01.private void performTraversals() {
02. // cache mView since it is used so much below...
03. final View host = mView;
04.
05. mTraversalScheduled = false;
06. boolean surfaceChanged = false;
07. WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = mWindowAttributes;
08.
09. int desiredWindowWidth; //表示该窗口期望width值
10. int desiredWindowHeight; //表示该窗口期望width值
11. int childWidthMeasureSpec; //保存root View的widthMeasureSpec
12. int childHeightMeasureSpec; //保存root View的heightMeasureSpec
13.
14. final View.AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
15.
16. final int viewVisibility = getHostVisibility();
17. boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility
18. || mNewSurfaceNeeded;
19.
20. float appScale = mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale;
21.
22. WindowManager.LayoutParams params = null;
23. if (mWindowAttributesChanged) {
24. mWindowAttributesChanged = false;
25. surfaceChanged = true;
26. params = lp;
27. }
28. Rect frame = mWinFrame;
29. if (mFirst) { //mFirst表示是否是第一次绘制该Window
30. fullRedrawNeeded = true;
31. mLayoutRequested = true;
32.
33. DisplayMetrics packageMetrics =
34. mView.getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
35. //第一次绘制时desiredWindowWidth,desiredWindowHeight 值大小为屏幕大小
36. desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
37. desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
38. ...
39. } else { //不是第一次绘制,则desiredWindowWidth值为frame保存大小,frame值会由WMS填充
40. desiredWindowWidth = frame.width();
41. desiredWindowHeight = frame.height();
42. ...
43. }
44. ...
45. boolean insetsChanged = false;
46.
47. if (mLayoutRequested) {
48. ...//获得root View的widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec值
49. childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
50. childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
51. //开始measure过程
52. host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
53. }
54. ...
55. final boolean didLayout = mLayoutRequested;
56.
57. boolean triggerGlobalLayoutListener = didLayout
58. || attachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes;
59. if (didLayout) {
60. ... //layout过程
61. host.layout(0, 0, host.mMeasuredWidth, host.mMeasuredHeight);
62. ...
63. }
64. ...
65. if (!cancelDraw && !newSurface) {
66. mFullRedrawNeeded = false;
67. draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
68. ...
69.} |
01./**
02. * @param windowSize The available width or height of the window
03. *
04. * @param rootDimension The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the window.
05. */
06. private int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
07. int measureSpec;
08. switch (rootDimension) {
09. case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
10. // Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
11. measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
12. break;
13. case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
14. // Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
15. measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
16. break;
17. default:
18. // Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
19. measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
20. break;
21. }
22. return measureSpec;
23. } |
调用root View的measure()方法时,其参数是由getRootMeasureSpec()设置的,基本思路同我们前面描述的
差不多。贴出来的代码只是简简单单列出了measure 、layout
、 draw 过程的调用点,里面有很多逻辑处理, |


