| 示例说明
本篇的例子的是一个在线订票的服务系统。这个系统向外界暴露了一些可以通过Http协议访问的API,在这个订票服务下面允许任意多个隶属机构来使用服务API进行真正的售票活动。如下图所示
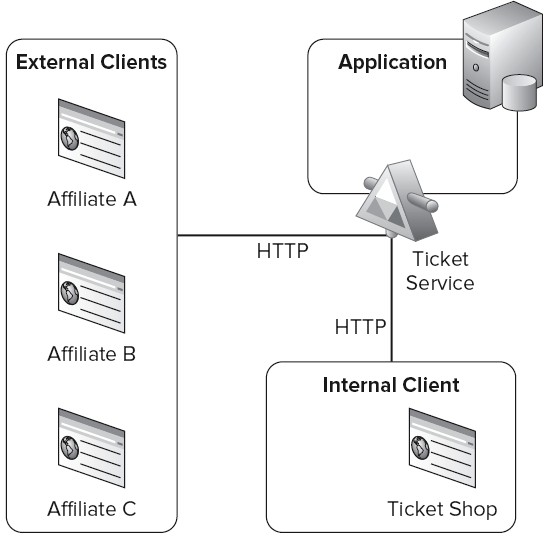
就好比银行外面的那些自动取款机(对应图中的Affiliate A, B, C),可以把它们看成是银行系统的隶属机构,我们就是通过这些取款机来进行存取活动的,其实这些取款机是调用了银行系统的一些服务来进行数据操作,当然我们也可以直接到银行柜台(对应图中的Ticket
Shop)去进行存取款操作。本例中的售票例子和这个有点类似。
在本例中,在我们将会在上图中的Application和Internal Client之间采用Reservation模式来约定票,通过采用Idempotent模式来确保订票的每个交易只进行一次。
下面就开始进入实战:
解决方案建立如下:
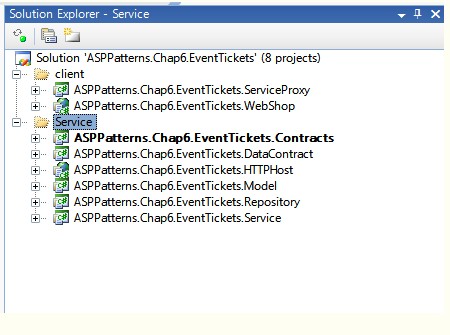
为了演示的方便,上面的Solution把客户端和服务端程序建立在了一起。
Domain Model
首先,我们来建立这个系统中所涉及到的一些业务类和一些辅助的类。
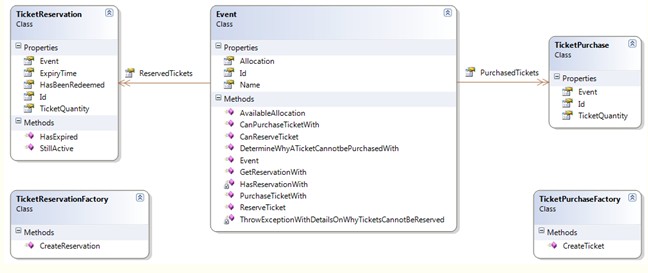
其中:
Event类代表了一次购票的活动。
Event类包含了两个集合:一个TicketPurchase集合代表了真实的要购买的票;另外一个TicketReservation集合代表了Reservation模式中的预约票据,或者大家理解为标识,或者令牌,概念类似于ASP.NET中的验证票据
。
另外两个工厂类提供了一些简单的接口来创建TicketPurchase和TicketReservation。
下面我们就来看看上面提及的一些类的具体的定义:
TicketReservation代码
public class TicketReservation
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public Event Event { get; set; }
public DateTime ExpiryTime { get; set; }
public int TicketQuantity { get; set; }
public bool HasBeenRedeemed { get; set; }
public bool HasExpired()
{
return DateTime.Now > ExpiryTime;
}
public bool StillActive()
{
return !HasBeenRedeemed && !HasExpired();
}
}
TicketPurchase代码
public class TicketPurchase
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public Event Event { get; set; }
public int TicketQuantity { get; set; }
}
为了简化创建票据类的方面,我们添加两个工厂类:如下:
public class TicketReservationFactory
{
public static TicketReservation CreateReservation(Event
Event, int tktQty)
{
TicketReservation reservation = new TicketReservation();
reservation.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
reservation.Event = Event;
reservation.ExpiryTime = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(1);
reservation.TicketQuantity = tktQty;
return reservation;
}
}
public class TicketPurchaseFactory
{
public static TicketPurchase CreateTicket(Event Event,
int tktQty)
{
TicketPurchase ticket = new TicketPurchase();
ticket.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
ticket.Event = Event;
ticket.TicketQuantity = tktQty;
return ticket;
}
}
上面两个工厂的方法都是很直观,简单。在TicketReservationFactory中创建ReservationTicket类的时候,设置这个标识票据的默认过期时间是一分钟。也就是说,整个订票的交易要在一分钟之内完成,当然一分钟只是例子而已,便于例子的测试。可能时间太长了一是耗费太多的资源,二是在安全方面也存在一些隐患。
下面就来一起看看比较核心的Event类:(下面的代码有点多,在代码的后面我会详细讲述类中每个方法的意思)
public class Event
{
public Event()
{
ReservedTickets = new List<TicketReservation>();
PurchasedTickets = new List<TicketPurchase>();
}
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Allocation { get; set; }
public List<TicketReservation> ReservedTickets
{ get; set; }
public List<TicketPurchase> PurchasedTickets {
get; set; }
public int AvailableAllocation()
{
int salesAndReservations = 0;
PurchasedTickets.ForEach(t => salesAndReservations
+= t.TicketQuantity);
ReservedTickets.FindAll(r => r.StillActive()).ForEach(r
=> salesAndReservations += r.TicketQuantity);
return Allocation - salesAndReservations;
}
public bool CanPurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (HasReservationWith(reservationId))
return GetReservationWith(reservationId).StillActive();
return false;
}
public TicketPurchase PurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (!CanPurchaseTicketWith(reservationId))
throw new ApplicationException(DetermineWhyATicketCannotbePurchasedWith(reservationId));
TicketReservation reservation = GetReservationWith(reservationId);
TicketPurchase ticket = TicketPurchaseFactory.CreateTicket(this,
reservation.TicketQuantity);
reservation.HasBeenRedeemed = true;
PurchasedTickets.Add(ticket);
return ticket;
}
public TicketReservation GetReservationWith(Guid reservationId)
{
if (!HasReservationWith(reservationId))
throw new ApplicationException(String.Format("No
reservation ticket with matching id of '{0}'",
reservationId.ToString()));
return ReservedTickets.FirstOrDefault(t => t.Id
== reservationId);
}
private bool HasReservationWith(Guid reservationId)
{
return ReservedTickets.Exists(t => t.Id == reservationId);
}
public string DetermineWhyATicketCannotbePurchasedWith(Guid
reservationId)
{
string reservationIssue = "";
if (HasReservationWith(reservationId))
{
TicketReservation reservation = GetReservationWith(reservationId);
if (reservation.HasExpired())
reservationIssue = String.Format("Ticket reservation
'{0}' has expired", reservationId.ToString());
else if (reservation.HasBeenRedeemed )
reservationIssue = String.Format("Ticket reservation
'{0}' has already been redeemed", reservationId.ToString());
}
else
reservationIssue = String.Format("There is no ticket
reservation with the Id '{0}'", reservationId.ToString());
return reservationIssue;
}
private void ThrowExceptionWithDetailsOnWhyTicketsCannotBeReserved()
{
throw new ApplicationException("There are no tickets
available to reserve.");
}
public bool CanReserveTicket(int qty)
{
return AvailableAllocation() >= qty;
}
public TicketReservation ReserveTicket(int tktQty)
{
if (!CanReserveTicket(tktQty))
ThrowExceptionWithDetailsOnWhyTicketsCannotBeReserved();
TicketReservation reservation = TicketReservationFactory.CreateReservation(this,
tktQty);
ReservedTickets.Add(reservation);
return reservation;
}
}
下面,我们就来看看每个方法的作用:
AvailableAllocation():这个方法计算现有还有多少票可以卖;用总的票数减去已经卖出的票数和已经预定了的票数。
CanReserveTicket(int qty):这个检查是否还有足够数量的票供预定。
ReserveTicket(int qty): 这个方法创建一个新的TicketReservation,并且指定在这个标识票据中有多少张真实的票要购买的,并且将标识票据添加到集合中
HasReservationWith(Guid reservationId):这个方法判断给定Id的TicketReservation是否存在。
GetReservationWith(Guid reservationId):通过Id标识,获取一个TicketReservation。
CanPurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId):这个方法判断可以基于给定的标识Id来购买真实的票。
PurchaseTicketWith(Guid reservationId):基于给的预约标识来创建一个新的真实的票TicketPurchase.
DetermineWhyTicketCannotBePurchase(Guid reservationId):这个方法返回一个字符串结果,说明一下为什么不能基于给定的预约标识来购买票,可以因为标识过期或者我们规定一个标识所代表的一次交易最多只能买指定数量的真实票。
业务类建立完成之后,下面我们就来创建一个类来进行存取这些业务类所需要的数据。
Repository
添加一个IEventReposistory接口,如下:
public interface IEventRepository
{
Event FindBy(Guid id);
void Save(Event eventEntity);
}
为了演示的简洁,这个接口定义的很简单。下面就用ADO.NET的方式来实现一个EventRepository.(当然,大家可以采用自己喜欢的数据访问技术)
下面的代码很多,但是很容易理解:
public class EventRepository : IEventRepository
{
private string connectionString = @"Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\EventTickets.mdf;Integrated
Security=True;User Instance=True";
public Event FindBy(Guid id)
{
Event Event = default(Event);
string queryString = "SELECT * FROM dbo.Events
WHERE Id = @EventId " +
"SELECT * FROM dbo.PurchasedTickets WHERE EventId
= @EventId " +
"SELECT * FROM dbo.ReservedTickets WHERE EventId
= @EventId;";
using (SqlConnection connection =
new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand command = connection.CreateCommand();
command.CommandText = queryString;
SqlParameter Idparam = new SqlParameter("@EventId",
id.ToString());
command.Parameters.Add(Idparam);
connection.Open();
using (SqlDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader())
{
if (reader.HasRows)
{
reader.Read();
Event = new Event();
Event.PurchasedTickets = new List<TicketPurchase>();
Event.ReservedTickets = new List<TicketReservation>();
Event.Allocation = int.Parse(reader["Allocation"].ToString());
Event.Id = new Guid(reader["Id"].ToString());
Event.Name = reader["Name"].ToString();
if (reader.NextResult())
{
if (reader.HasRows)
{
while (reader.Read())
{
TicketPurchase ticketPurchase = new TicketPurchase();
ticketPurchase.Id = new Guid(reader["Id"].ToString());
ticketPurchase.Event = Event;
ticketPurchase.TicketQuantity = int.Parse(reader["TicketQuantity"].ToString());
Event.PurchasedTickets.Add(ticketPurchase);
}
}
}
if (reader.NextResult())
{
if (reader.HasRows)
{
while (reader.Read())
{
TicketReservation ticketReservation = new TicketReservation();
ticketReservation.Id = new Guid(reader["Id"].ToString());
ticketReservation.Event = Event;
ticketReservation.ExpiryTime = DateTime.Parse(reader["ExpiryTime"].ToString());
ticketReservation.TicketQuantity = int.Parse(reader["TicketQuantity"].ToString());
ticketReservation.HasBeenRedeemed = bool.Parse(reader["HasBeenRedeemed"].ToString());
Event.ReservedTickets.Add(ticketReservation);
}
}
}
}
}
}return Event;
}
public void Save(Event Event)
{
// Code to save the Event entity
// is not required in this senario
RemovePurchasedAndReservedTicketsFrom(Event);
InsertPurchasedTicketsFrom(Event);
InsertReservedTicketsFrom(Event);
}
public void InsertReservedTicketsFrom(Event Event)
{
string insertSQL = "INSERT INTO ReservedTickets
" +
"(Id, EventId, TicketQuantity, ExpiryTime, HasBeenRedeemed)
" +
"VALUES " +
"(@Id, @EventId, @TicketQuantity, @ExpiryTime,
@HasBeenRedeemed);";
foreach (TicketReservation ticket in Event.ReservedTickets)
{
using (SqlConnection connection =
new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand command = connection.CreateCommand();
command.CommandText = insertSQL;
SqlParameter Idparam = new SqlParameter("@Id",
ticket.Id.ToString());
command.Parameters.Add(Idparam);
SqlParameter EventIdparam = new SqlParameter("@EventId",
ticket.Event.Id.ToString());
command.Parameters.Add(EventIdparam);
SqlParameter TktQtyparam = new SqlParameter("@TicketQuantity",
ticket.TicketQuantity);
command.Parameters.Add(TktQtyparam);
SqlParameter Expiryparam = new SqlParameter("@ExpiryTime",
ticket.ExpiryTime);
command.Parameters.Add(Expiryparam);
SqlParameter HasBeenRedeemedparam = new SqlParameter("@HasBeenRedeemed",
ticket.HasBeenRedeemed);
command.Parameters.Add(HasBeenRedeemedparam);
connection.Open();
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
public void InsertPurchasedTicketsFrom(Event Event)
{
string insertSQL = "INSERT INTO PurchasedTickets
" +
"(Id, EventId, TicketQuantity) " +
"VALUES " +
"(@Id, @EventId, @TicketQuantity);";
foreach (TicketPurchase ticket in Event.PurchasedTickets)
{
using (SqlConnection connection =
new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand command = connection.CreateCommand();
command.CommandText = insertSQL;
SqlParameter Idparam = new SqlParameter("@Id",
ticket.Id.ToString());
command.Parameters.Add(Idparam);
SqlParameter EventIdparam = new SqlParameter("@EventId",
ticket.Event.Id.ToString());
command.Parameters.Add(EventIdparam);
SqlParameter TktQtyparam = new SqlParameter("@TicketQuantity",
ticket.TicketQuantity);
command.Parameters.Add(TktQtyparam);
connection.Open();
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
public void RemovePurchasedAndReservedTicketsFrom(Event
Event)
{
string deleteSQL = "DELETE PurchasedTickets WHERE
EventId = @EventId; " +
"DELETE ReservedTickets WHERE EventId = @EventId;";
using (SqlConnection connection =
new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand command = connection.CreateCommand();
command.CommandText = deleteSQL;
SqlParameter Idparam = new SqlParameter("@EventId",
Event.Id.ToString());
command.Parameters.Add(Idparam);
connection.Open();
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
今天就到这里。下一篇接着讲述!
| 

